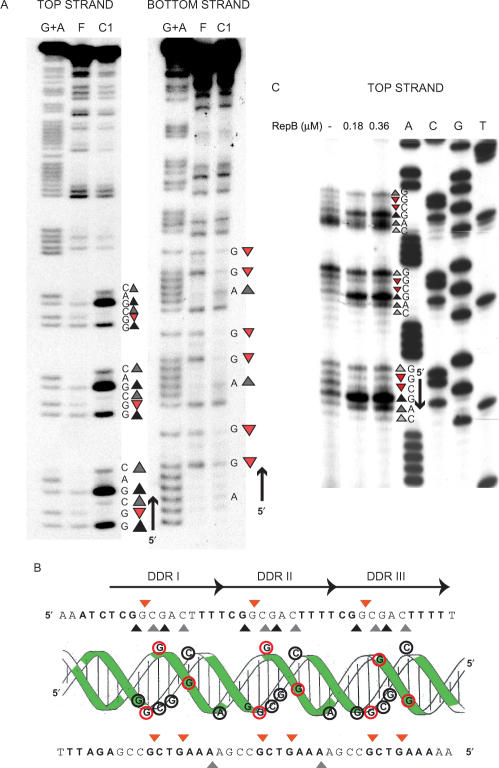
Figure 3.
High resolution contacts of RepB with the bind locus. (A) DMS footprint of RepB bound to a linear DNA fragment containing the DDR. Bases hypermethylated (grey or black triangles, depending on whether there is a slight or a marked increase, respectively, in the DMS sensitivity) or protected (red triangles) in each strand by bound RepB are shown. To the right, the DNA sequence of the footprinted regions is displayed with its 5′→3′ directionality. Lanes: F, free DNA; C1, DNA of complex C1; G+A, Maxam and Gilbert sequencing ladder for purines. (B) Scheme of the B-DNA double helix of the DDR displayed with the nucleotide sequences of the top and bottom strands. Bases whose deoxyriboses are protected by RepB against HO• attack are shown in boldface letters or as green-shadowed regions on the double helix. Bases which become hypermethylated (grey/black triangles, black-lined encircled letters) or protected from methylation (red triangles, red-lined encircled letters) upon binding of RepB are indicated on the sequence and on the DNA double helix. The three repeats constituting the DDR are indicated by arrows. (C) DMS footprint of RepB bound to the DDR on supercoiled pMV158. The methylation sites on the top strand were mapped by primer extension using labelled primer dso4 corresponding to the bottom strand. The same primer was used for the control dideoxy sequencing ladder (lanes A, C, G, T). The methylation pattern of the bind locus was obtained in the absence of RepB or at the indicated concentrations of the protein. To the right, the DNA sequence at the footprinted regions is displayed with its 5′→3′ directionality. The same symbol code as in A was used.