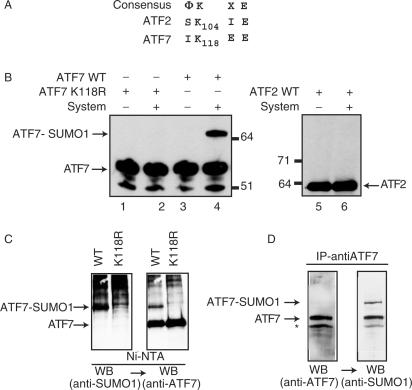
Figure 1.
SUMO-1 modification of recombinant ATF proteins. Peptide sequence alignments between ATF7 and ATF2. (A) Amino acid sequences (one-letter code) of relevant portions of the proteins are given, below the consensus sumoylation target site (Φ, hydrophobic residues; X, any residue). Bold-faced characters represent potential sumoylation sites, with respective coordinates. (B) Purified bacterially expressed ATF7 WT (lanes 3 and 4), ATF7 K118R (lanes 1 and 2) and in vitro synthesized 35S-labeled ATF2 (lanes 5 and 6) were subjected to in vitro SUMO-1 conjugation, as indicated (System refers to the complete assay reaction as described in Materials and Methods—AU refers to arbitrary unit). Reaction products were analyzed by SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting using ATF7 (2F10) monoclonal-antibodies (lanes 1–4) or autoradiography (lanes 5 and 6). (C) HeLa-SUMO cells were transfected with 0.5 µg px-ATF7WT or pXATFK118R. Extracts (500 µg) from transfected cells were passed through Ni-NTA agarose (affinity-purification). Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and the presence of sumoylated ATF7, and then ATF7 was revealed by western blotting (WB) using specific antibodies, as indicated. (D) Extracts (500 µg) from Raji cells were immunoprecipitated with the anti-ATF7 (2F10) antibodies. Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and the presence of ATF7, and then sumoylated ATF7 was revealed by western blotting (WB) using specific antibodies, as indicated.