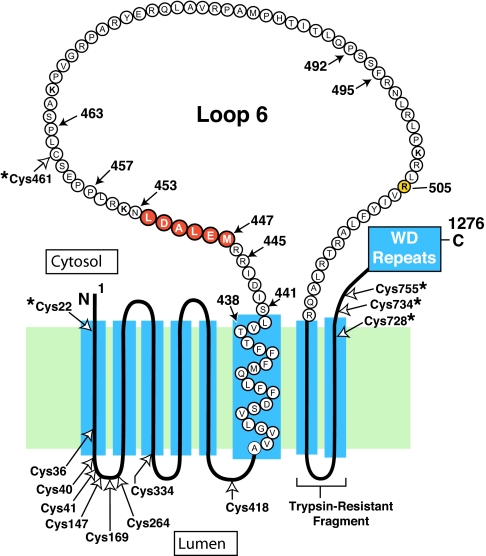
Fig. 1.
Amino acid sequence and topology of the membrane domain of hamster Scap. The cytoplasmic loop between transmembrane helices 6 and 7 is referred to as loop 6, and it is postulated to extend from Ser-441 to Arg-518. Amino acids 447–452 (highlighted in red) constitute the hexapeptide sequence MELADL. Filled arrows denote amino acids that were mutated in the current experiments. Open arrows denote all of the cysteine residues in the membrane domains of Scap; those cysteines marked by asterisks (*) were changed to alanines to create the Cys(−) construct used as the parent plasmid for the experiments in Fig. 4. Arg-505 (highlighted in yellow) denotes a cholesterol-induced, trypsin-sensitive cleavage site (20, 21). Trypsin-resistant fragment denotes the sequence between membrane helices 7 and 8 (amino acids 540–707) that is detected by IgG-R139 (33).