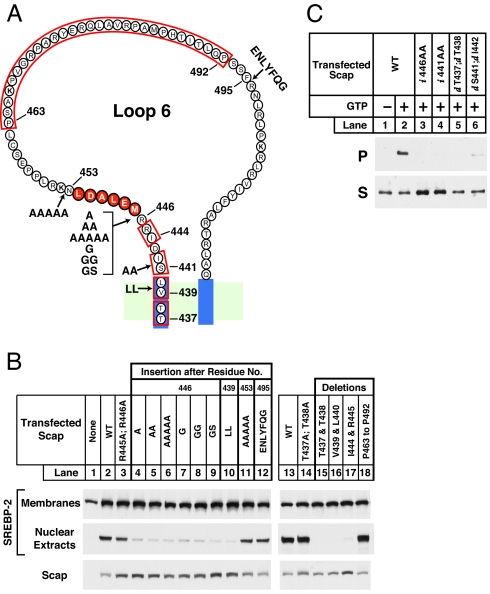
Fig. 5.
Amino acid insertions or deletions adjacent to MELADL sequence alter Scap function. (A) Amino acid sequence of loop 6 of Scap, showing sites of insertions (arrows) and deletions (red box). (B and C) On day 0, Scap-deficient SRD-13A cells were set up in 60-mm dishes. (B) SREBP-2 cleavage. On day 2, cells were transfected with 2.5 μg of pTK-SREBP-2 and 0.2 μg of the indicated wild-type or mutant version of pCMV–Scap. Twelve hours after transfection, cells were switched to sterol-depleting medium with 1% HPCD and incubated for 1 h at 37°C. Cells were then incubated with sterol-depleting medium (without HPCD) for 3 h at 37°C and harvested for preparation of nuclear extract and membrane fractions. These fractions were subjected to 8% SDS/PAGE and immunoblot analysis with anti-HSV IgG (anti-SREBP-2) and IgG-R139 (anti-Scap) as indicated. (C) Flag-Sec23 pulldown. On day 2, cells were transfected with 0.4 μg of wild-type or the indicated mutant version of pCMV–Scap (i, insertion; d, deletion). Twelve hours after transfection, cells were treated the same as in B and harvested. Microsomal membranes (150 μg) were analyzed for Scap binding to COPII proteins using the Flag-Sec23 pull-down assay as described in Fig. 2A. Supernatant (S) and pellet (P) (5% of S) fractions were subjected to 8% SDS/PAGE and immunoblot analysis with IgG-R139 (anti-Scap).