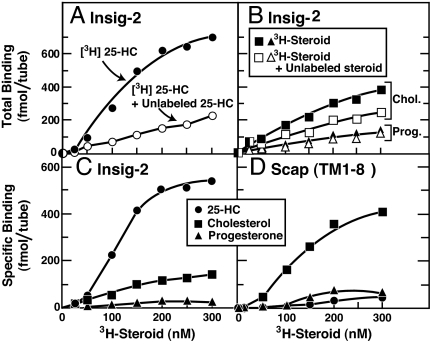
Fig. 2.
Steroid specificity of binding to Insig-2 (A–C) and Scap(TM1–8) (D). (A and B) Total binding of [3H]steroids to Insig-2. Each assay tube, in a total volume of 100 μl of buffer A, contained 400 nM His10–Insig-2–FLAG (40 pmol), 25 mM phosphocholine chloride, and varying concentrations of the indicated [3H]steroid [[3H]25-HC (152 dpm/fmol) (A), [3H]cholesterol (120 dpm/fmol) (B), or [3H]progesterone (215 dpm/fmol) (B)] in the absence (filled symbols) or presence (open symbols) of the respective unlabeled steroid at a final concentration of 5 μM. After incubation for 4 h at room temperature, bound [3H]steroids were measured as described in Materials and Methods. Each data point is the average of duplicate assays and represents the total binding without subtraction of any blank values. (C) Specific binding of [3H]steroids to Insig-2. These data are replotted from A and B. (D) Specific binding of [3H]steroids to Scap(TM1–8). Each assay was carried out as described in A and B except that the tubes contained 120 nM His10–Scap(TM1–8) (12 pmol) instead of His10–Insig-2–Flag. Each data point is the average of duplicate assays. Specific binding in C and D was calculated by subtracting the binding value in the presence of unlabeled steroid from that in its absence.