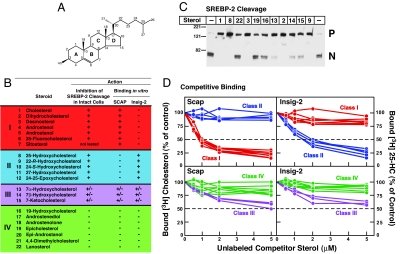
Fig. 3.
Differential sterol specificity for Insig-2 and Scap: comparison of binding in vitro and inhibition of SREBP-2 cleavage in mammalian cells. (A) Chemical structure of cholesterol. (B) List of sterols tested and their actions in inhibiting SREBP-2 cleavage in intact cells and in competing with the binding of [3H]cholesterol to Scap and of [3H]25-HC to Insig-2. The degree of effect (maximal, intermediate, or minimal) is denoted by +, +/−, and −, respectively. For assays of SREBP-2 cleavage, 11 sterols (each at a final concentration of 20 μM in a 1:12 molar ratio with MCD) were tested in the current study (see C). The data for all other steroids have been reported (20, 27). Sterol 7 (sitosterol) could not be solubilized in a 1:12 molar ratio with MCD. For binding assays, all 22 sterols were tested in the current study; representative competition curves are shown in D and E. Trivial sterol names and their standard nomenclature (other than for cholesterol and its derivatives) are as follows: dihydrocholesterol for 5α-cholestan-3β-ol (2); desmosterol, 5,24-cholestadien-3β-ol (3); androstenol, 5-androsten-3β-ol (4); androstanol, 5α-androstan-3β-ol (5); sitosterol, 5-cholesten-24β-ethyl-3β-ol (7); 17-androstenediol, 5-androsten-3β,17β-diol (17); androstenolone, 5-androsten-3β-ol-17-one (18); epicholesterol, 5-cholesten-3α-ol (19); epi-androstanol, 5α-androstan-3α-ol (20); and lanosterol, 8,24,(5α)-cholestadien-4,4,14α-trimethyl-3β-ol (22). (C) Immunoblot analysis of SREBP-2 cleavage in mammalian cells. On day 2, CHO-K1 cells were incubated for 1 h in medium D containing 1% HPCD and then switched to medium D containing the indicated sterol (20 μM) complexed to MCD. After incubation for 6 h, cells were harvested, and total cell extracts were immunoblotted with IgG-7D4 (anti-SREBP-2). The precursor and mature nuclear form of SREBP-2 are denoted by P and N, respectively. (D) Competitive binding of [3H]cholesterol to Scap (Left) and [3H]25-HC to Insig-2 (Right). Each assay tube, in a total volume of 100 μl of buffer A, contained 25 mM phosphocholine chloride, 120 nM His10–Scap(TM1–8) or 400 nM His10–Insig-2–FLAG as indicated, 100 nM [3H]cholesterol (120 dpm/fmol) or 100 nM [3H]25-HC (152 dpm/fmol) as indicated, and varying concentration of the indicated unlabeled sterol. After incubation for 4 h at room temperature, bound [3H]cholesterol or [3H]25-HC was measured as described in Materials and Methods. Each data point is the average of duplicate assays and represents the amount of [3H]cholesterol or [3H]25-HC bound relative to that in the control tube, which contained no unlabeled sterol. In a typical competition experiment, six to nine unlabeled sterols were tested, two of which were always cholesterol and 25-HC. “100% of control” values for [3H]cholesterol binding (Left) ranged from 209 to 263 fmol per tube in four experiments. “100% of control” values for [3H]25-HC binding (Right) ranged from 199 to 261 fmol per tube in four experiments. All unlabeled sterols were tested in duplicate in two or more experiments with similar results.