Figure 2.
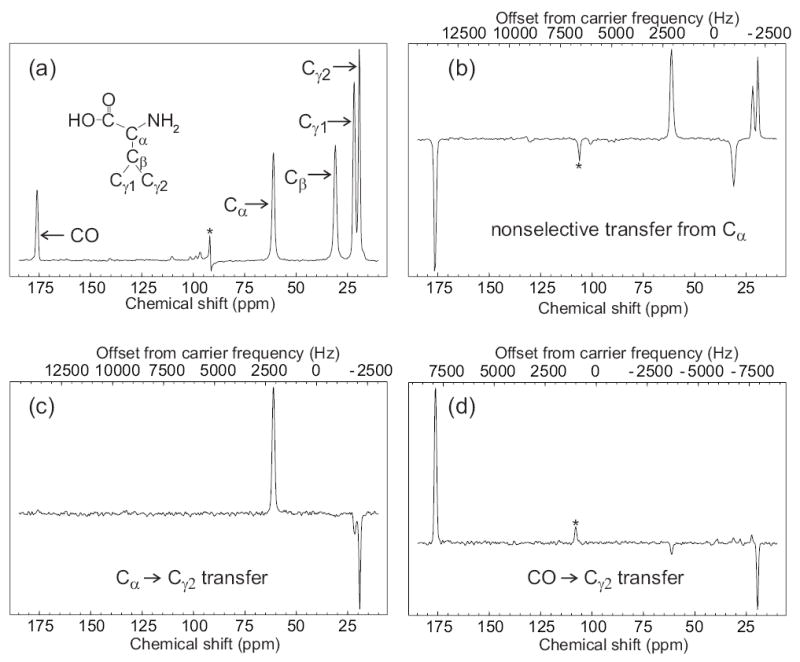
Demonstration of frequency-selective polarization transfer in uniformly 15N,13C-labeled L-valine powder under SEASHORE, using the POST-C7 recoupling technique. (a) Conventional 13C NMR spectrum with peak assignments, obtained at 100.4 MHz 13C NMR frequency with 8.000 kHz MAS. (b) Spectrum obtained with the pulse sequence in Fig. 1, with selective excitation of the Cα peak, N = 8, m = 2, n = 0, and 7.000 kHz MAS. (c) Spectrum obtained with selective excitation of the Cα peak, N = 14, m = 2, n = 3, and 7.288 kHz MAS. (d) Spectrum obtained with selective excitation of the CO peak, N = 26, m = 2, n = 4, and 6.878 kHz MAS. All spectra were obtained with 16 scans at 100.4 MHz 13C NMR frequency, using a 10 mg sample, and 110 kHz proton decoupling throughout the Gaussian-shaped pulse, SEASHORE recoupling, and signal acquisition. For parts c and d, rf carrier frequencies during the SEASHORE period were set to the midpoint of the 13C NMR frequencies of the spin pair of interest. Values of n and the MAS frequency were chosen to optimize the selectivity of dipolar recoupling. Asterisks indicate an artifact at the carrier frequency in part a and MAS sideband lines in parts b and c.
