Figure 6.
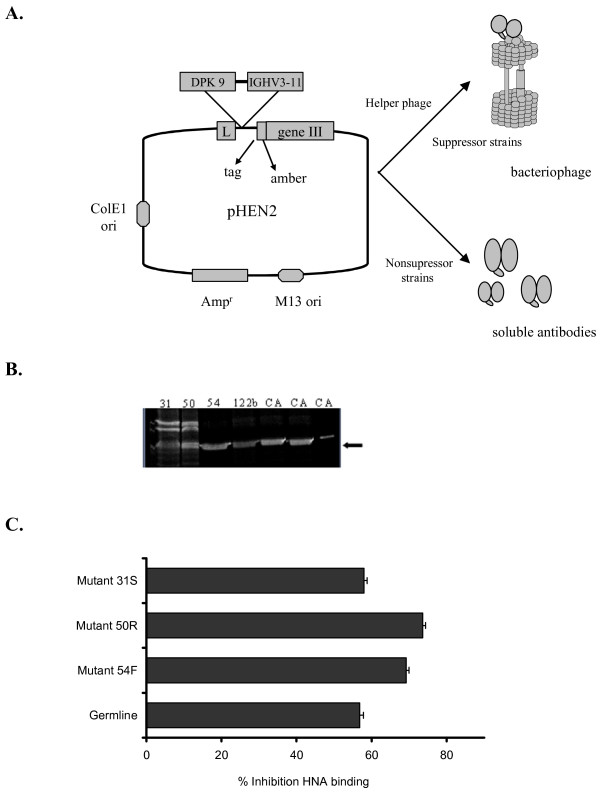
Single chain xenoantibodies were produced using the pHEN vector and expressed as soluble antibodies. The xenoantibodies with site-directed mutations were compared with the germline progenitor for the ability to inhibit natural antibody binding. (A.) The IGHV3-11 gene encoding xenoantibodies in human patients was cloned into the vector pHEN2. Single chain xenoantibodies were expressed as phagemid or soluble antibodies for functional studies. (B.) The soluble antibodies were run on an SDS page gel to confirm that antibody was produced. (C.) The ability of the soluble single chain antibodies with specific site-directed mutations to block human xenoantibody binding was compared by inhibition ELISA. The ability to bind more efficiently to purified gal carbohydrate, and thereby block human xenoantibody binding more effectively was compared in this assay. Single chain antibodies with a mutation at site 50 block the binding of human xenoantibodies most effectively.
