Figure 5.
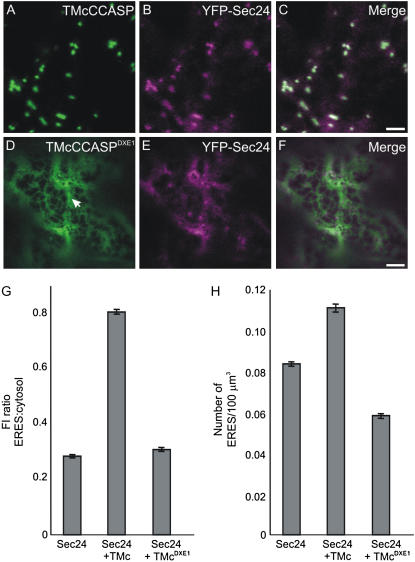
Mutation of a cytosolic diacidic motif prevents recruitment of YFP-Sec24 to ERES. A to C, TMcCCASP (A) predominantly labels the Golgi apparatus. Coexpression with YFP-Sec24 (B) leads to an apparent increase in both YFP fluorescence intensity at ERES and ERES number. C, Merged image of A and B. D to F, Mutation of a diacidic motif in TMcCCASP results in redistribution of the marker to the ER membranes (D, arrow). Coexpression of TMcCCASPDXE1 with YFP-Sec24 (E) does not noticeably affect YFP fluorescence intensity or ERES number. F, Merged image of D and E. Bars = 5 μm. G, Quantification of the YFP fluorescence intensity at ERES relative to that in the cytosol, shown as a ratio, indicates that in the presence of TMcCCASP (TMc), the fluorescence intensity at ERES increases relative to that of YFP-Sec24 alone. In comparison, no obvious increase in fluorescence intensity is observed on coexpression of TMcCCASPDXE1 (TMcDXE1). Fluorescence was measured for at least 10 ERES and cytosol areas per cell, giving an average of 1,500 ERES for each combination of markers. H, Number of ERES per 100 μm3 (sample size = 150 cells) expressing YFP-Sec24 in the presence of TMcCCASP increases in comparison to cells expressing YFP-Sec24 alone. However, coexpression of the export-incompetent TMcCCASPDXE1 slightly reduces the number of ERES per 100 μm3. Error bars represent se of the mean.