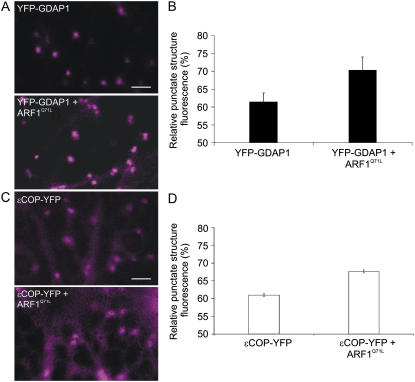
Figure 2.
Coexpression of active ARF1 and GDAP1 enhances the recruitment of the golgin onto the Golgi apparatus. A, Confocal images of the YFP channel only of cells expressing either YFP-GDAP1 alone or YFP-GDAP1 with untagged ARF1Q71L, which mimics the active form of ARF1 (Teal et al., 1994; Pimpl et al., 2000). The presence of untagged ARF1 in cells was ensured by using a double cistronic vector encoding ARF1Q71L and the peroxisomal marker, CFP-SKL (Stefano et al., 2006a). Fluorescence quantification was carried out in cells where both the YFP and CFP signals were present. Scale bar = 5 μm. B, The fluorescence of the punctate structures relative to that of the cytosol was quantified for YFP-GDAP1 alone or coexpressed with ARF1Q71L. The RPSF is given as a percentage of the ratio between fluorescence intensity values (arbitrary units) measured in the cytosol and the sum of intensity values for the cytosol and punctate structures (see “Materials and Methods”). We found that the intensity of punctate structure fluorescence increased significantly when YFP-GDAP1 was coexpressed with ARF1Q71L (P < 0.05). Error bars represent sds for 75 measurements over 45 different cells. C, Confocal images of cells expressing either ɛCOP-YFP alone or with untagged ARF1Q71L (YFP channel only) encoded in an ARF1Q71L-CFPSKL double cistronic vector, as described in A and B, above. D, Quantification of the RPSF fluorescence shows that in the presence of ARF1Q71L, the signal of ɛCOP-YFP increases on the Golgi membranes (P < 0.05). Error bars represent sds for 65 measurements over 30 different cells.