FIG. 1.
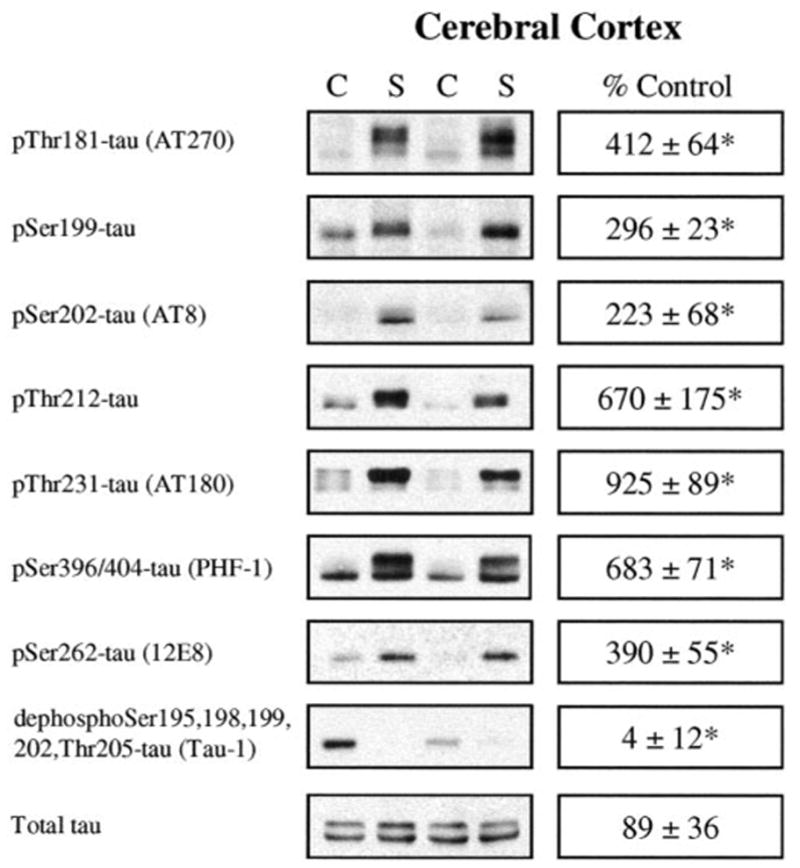
Streptozotocin administration caused multisite hyperphosphorylation of tau in mouse cerebral cortex. Mice were treated with streptozotocin, and after 3 days, protein extracts from the cerebral cortex were immunoblotted for phospho–Thr181-tau (AT270), phospho–Ser199-tau, phospho–Ser202-tau (AT8), phospho–Thr212-tau, phospho–Thr231-tau (AT180), phospho–Ser396/404-tau (PHF-1), phospho–Ser262-tau (12E8), dephospho–Ser195,198,199,202,Thr205-tau (tau-1; immunoreactivity increases as tau is dephosphorylated), and total tau. C, control; S, streptozotocin treated. Quantitative values were obtained by densitometric measurements of immunoblots and are means ± SE from four mice per group. *P < 0.05 compared with control values.
