Figure 1.
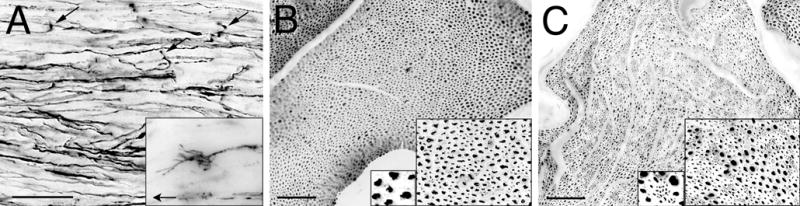
Intrafascicular retrograde regeneration (IRR) in rat sciatic nerve 28 weeks after transection and repair (direct epineurial neurorrhaphy). A) GAP-43 immunolabeling of regenerating axons in longitudinal section proximal to the repair site revealed many disoriented axons. Axonal sprouts were observed turning away from the repair site (arrows). Growth cones were found clearly oriented in the retrograde direction (inset; arrow points proximally). B) Transverse section of normal sciatic nerve showed a usual distribution of large and small diameter neurofilament immunolabeled axons. C) IRR was apparent proximal to the site of transection repair 28 weeks after injury by the appearance of clusters of small caliber, neurofilament-immunopositive axons (insets). Scale bars: A, 50 μm (inset: 4x); B and C, 100 μm (insets: 2x and 4x).
