Figure 3.
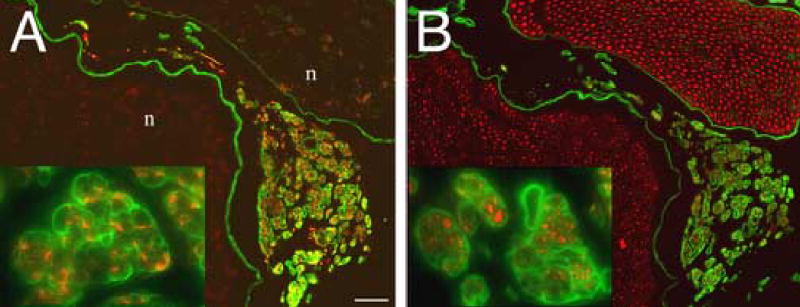
Definitive identification of ERR as GAP-43 immunoreactive axons within laminin labeled minifascicles. Transverse sections, 3mm proximal to the coaptation 28 weeks after nerve transection and repair, were double immunolabeled for (A) GAP-43 (growing axons, red) and laminin (basal laminae; green) or (B) neurofilament (all axons, red) and laminin (basal laminae, green). In (A), ERR minifascicles contain growing axons which express high levels of GAP-43 compared to unlabeled axons within the fascicles of the nerve proper (n). Laminin labeling revealed an intense immunoreactive basal laminae surrounding each ERR minifascicle (inset). In (B), a serial section from that in (A), neurofilament immunolabeling confirmed the identity of GAP-43 immunopositive profiles as axons and that only axons within ERR minifascicles express high levels of GAP-43. The lack of laminin labeling within the endoneurium of the nerve proper is an artifact of aldehyde fixation. As used here, laminin immunolabeling without antigen retrieval revealed the basal laminae of ERR minifascicles. Scale bars: A and B, 50 μm (insets: 4x).
