Figure 2.
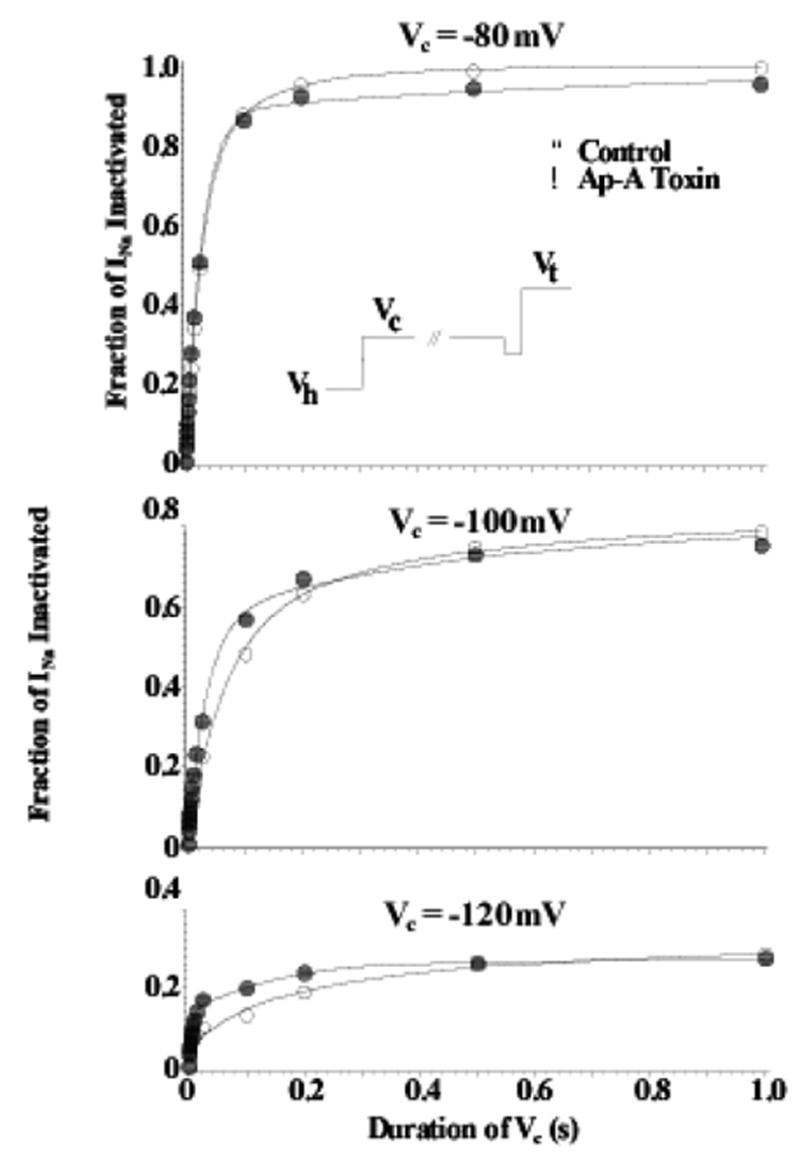
Closed-State Inactivation Remains Intact after Ap-A Toxin Modification of Na Channels. Shown are two-pulse development of inactivation relationships for Na channels in canine cardiac Purkinje cells at conditioning potentials (Vc) of −120 mV (bottom), −100 mV (middle), and −80 mV (top) in control (○) and after modification by Ap-A toxin (●). The voltage protocol is shown in the inset where the membrane potential was clamped-back to −110 or −120 mV for 2 ms before stepping to the test potential, Vt. Note that inactivation after Ap-A toxin occurs at least as fast as that in control at conditioning potentials negative to channel threshold. From Hanck and Sheets, 1995 with permission.
