Figure 3.
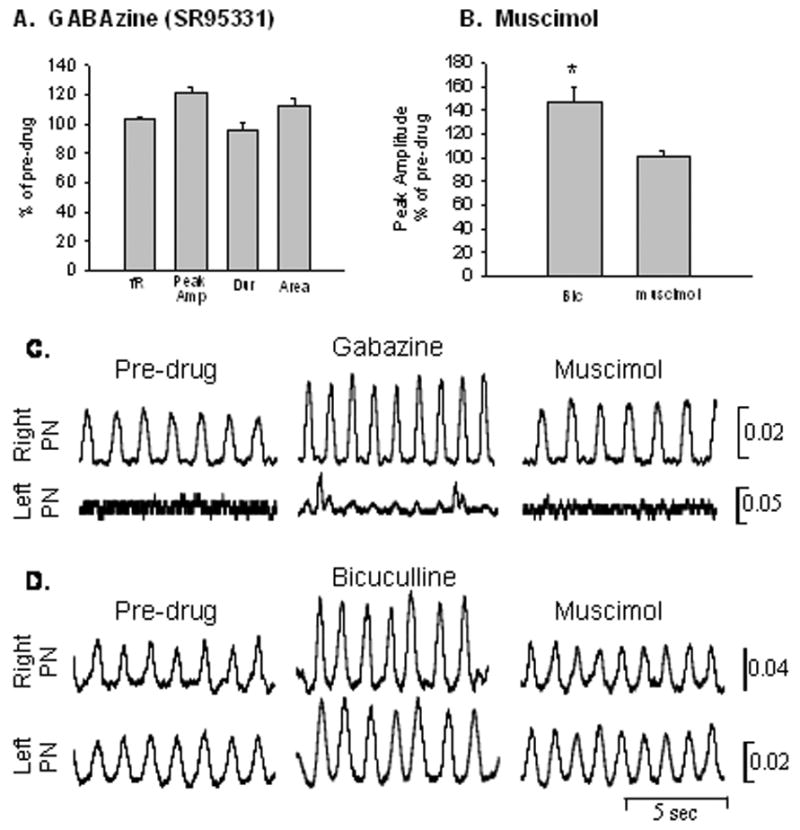
A. Gabazine application to the cervical spinal cord resulted in an increase in burst peak amplitude (peak Amp) and burst area (area), while there was no effect on frequency (fR) or burst duration (dur); similar to the effects observed with bicuculline application. B. Muscimol blocked the effects of bicuculline and peak amplitude was significantly reduced back to control values. C. Rectified and integrated traces of the respiratory motor output from one hemisected rat showing before drug, after Gabazine administration to the spinal cord followed by muscimol application. Note that Gabazine application induced crossed phrenic activity in the phrenic nerve ipsilateral to the hemisection and muscimol eliminated this effect. D. Rectified and integrated traces of the respiratory motor output from one control rat before drug, after bicuculline, and followed by muscimol application. Note that the peak amplitude of the phrenic bursts is increased after the GABA-A antagonist and this effect is blocked by muscimol.
