Figure 1.
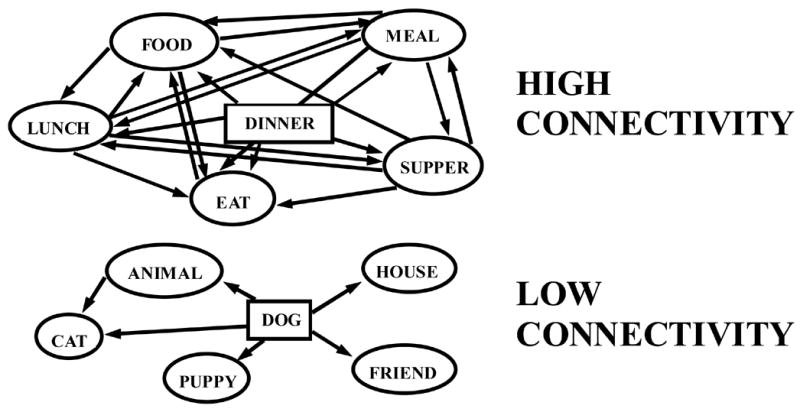
Examples of two lexical-semantic association networks that differ with respect to connectivity. The DINNER network is high in connectivity due to the greater number of associations that exist between associate words of the target word. The DOG network is low in connectivity due to the relatively fewer number of associations that exist between associate words of the target word.
