Figure 2. Actions of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) inhibitors on bile acid-induced MAPK phosphorylation and stimulation of H508 cell proliferation.
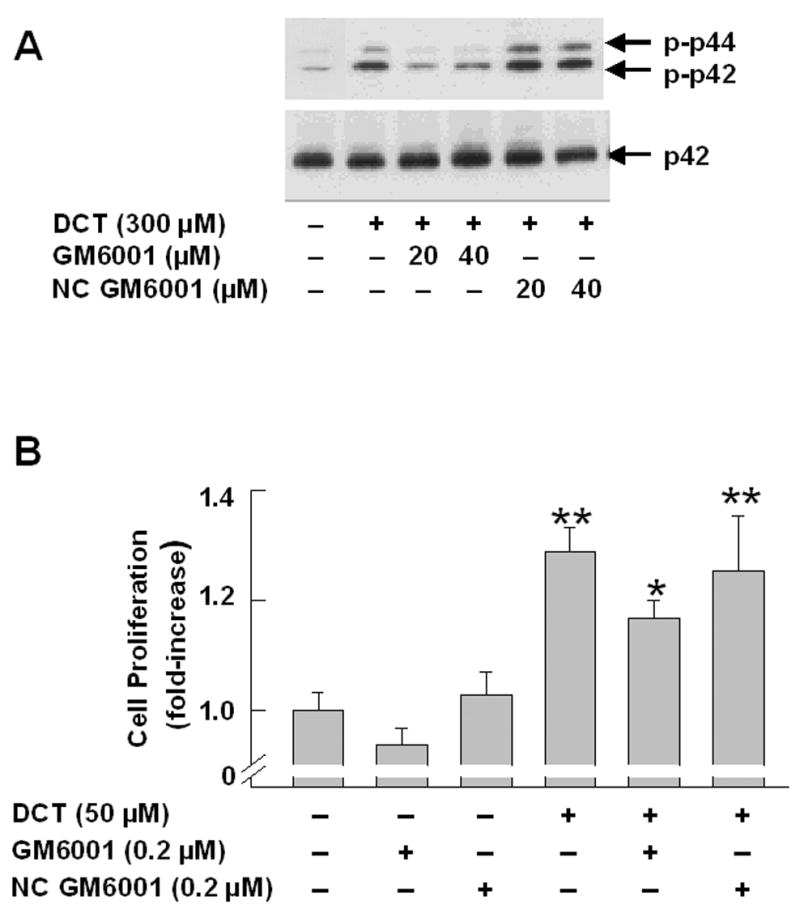
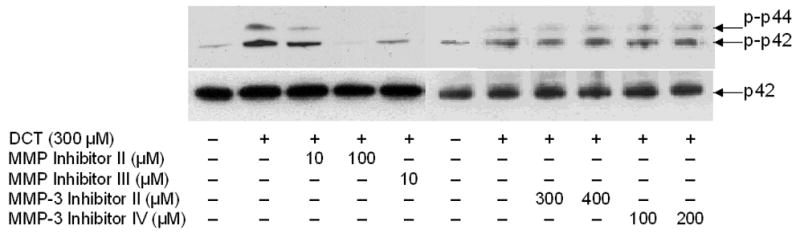
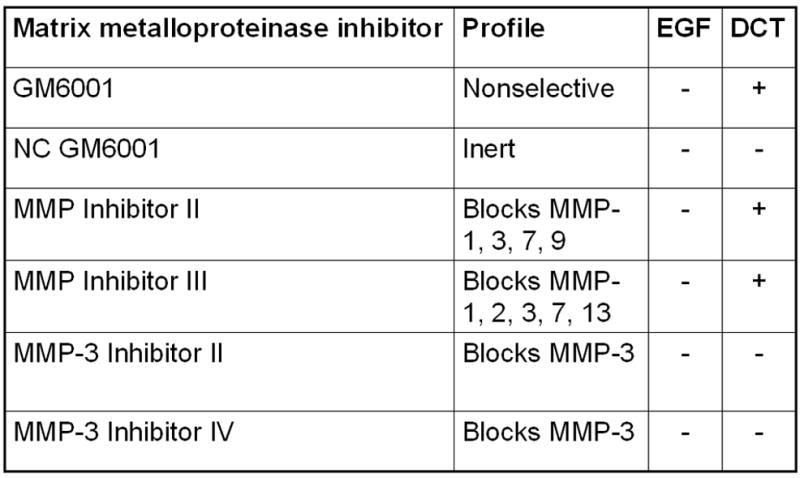
A. MAPK phosphorylation. H508 cells were treated with the indicated concentration of DCT for 10 minutes at 37°C, alone or with two concentrations of GM6001 and NC GM6001. p44/42 MAPK activity was determined by immunoblotting with antibodies specific for phosphorylated p44/42 MAPK. The quantity of protein added was verified by immunoblotting with antibodies specific for total p42 MAPK. Results are representative of 3 separate experiments. B. Cell proliferation. H508 cells were incubated with DCT, alone and with GM6001 or NC GM6001 for 5 days at 37°C. Cell proliferation was determined by the sulforhodamine blue (SRB) colorimetric assay [33]. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM of at least 3 experiments. *P < 0.05 vs cells stimulated with DCT alone. **P < 0.005 vs unstimulated cells. C. Actions of MMP Inhibitors II and III and MMP-3 Inhibitors II and IV on H508 cell proliferation. H508 cells were treated with 300 μM DCT for 10 minutes at 37°C, alone or with the indicated concentrations of MMP inhibitors II and III, and MMP-3 inhibitors II and IV. The quantity of protein added was verified by immunoblotting with antibodies specific for total p42 MAPK. Results are representative of 3 separate experiments. D. Profiles and actions of MMP inhibitors on EGF- and bile acid-induced phosphorylation of p44/42 MAPK in H508 human colon cancer cells. - indicates the inhibitor had no effect; + indicates inhibition by the inhibitor.
