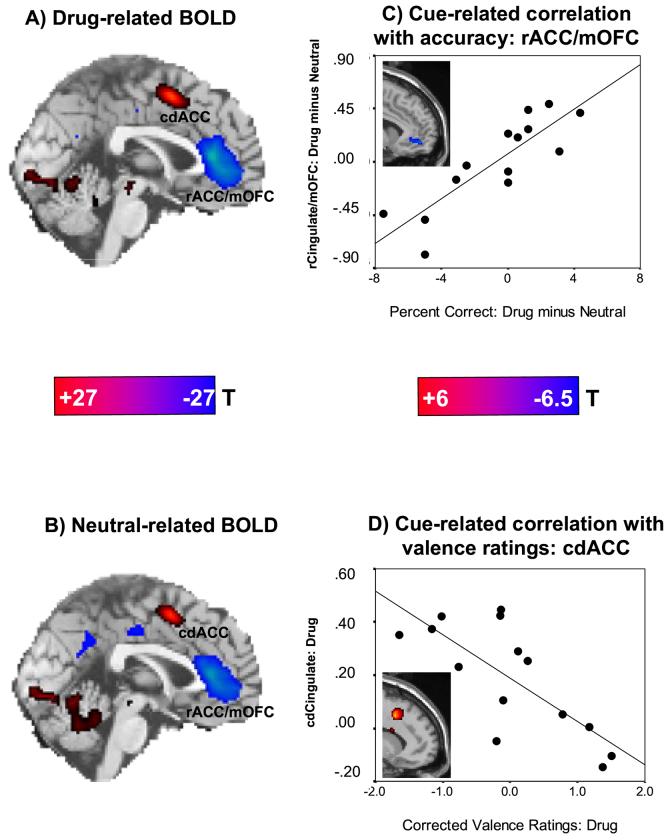
Figure 1.
Drug Stroop task: neural (BOLD) responses and correlations with behavior in 14 cocaine addicted individuals. A: A sagittal map is shown for cue-related activations (red: drug words > baseline) and hypoactivations (blue: drug words < baseline) (p < 0.05 family-wise corrected; color bar represents t-scores ≥ 7.99). B: A sagittal map is shown for neutral activations (red: neutral words > baseline) and hypoactivations (blue: neutral words < baseline) (p < 0.05 family-wise corrected; color bar represents t-scores ≥ 7.99); note that there were no significant differences in this pattern when directly comparing the word conditions (drug > neutral or drug < neutral; p < 0.01 uncorrected) for this sample (see also Figure 2s). C: The plot shows the association between the BOLD signal change for drug as compared to neutral words (drug > neutral) in the rACG/mOFC as a function of the respective differential performance accuracy and the corresponding linear regression line (r=0.85, p < 0.0001; x=6, y=51, z=-9); the inserted statistical map of brain activation depicts the cluster location corresponding to this correlation (p < 0.01 uncorrected; color bar represents t-scores ≥ 2.68; Table 2sC). D: The plot shows the association between the BOLD signal change for drug words as compared to baseline (drug > baseline) in the cdACG as a fuction of valence ratings for drug words and the corresponding linear regression line (r=-0.86, p < 0.0001; x=12, y=15, z=42); the inserted statistical map of brain activation depicts the cluster location corresponding to this correlation (p < 0.01 uncorrected; color bar represents t-scores ≥ 2.68; Table 2sD). Minimum cluster size was 50 contiguous voxels (1.35 cc) for all voxel-by-voxel analyses. cdACC is caudal-dorsal anterior cingulate cortex; rACC/mOFC is rostral anterior cingulate cortex/medial orbitofrontal cortex.