Figure 2. Brn3a is a direct regulator of the NeuroD4 gene in the embryonic trigeminal ganglion.
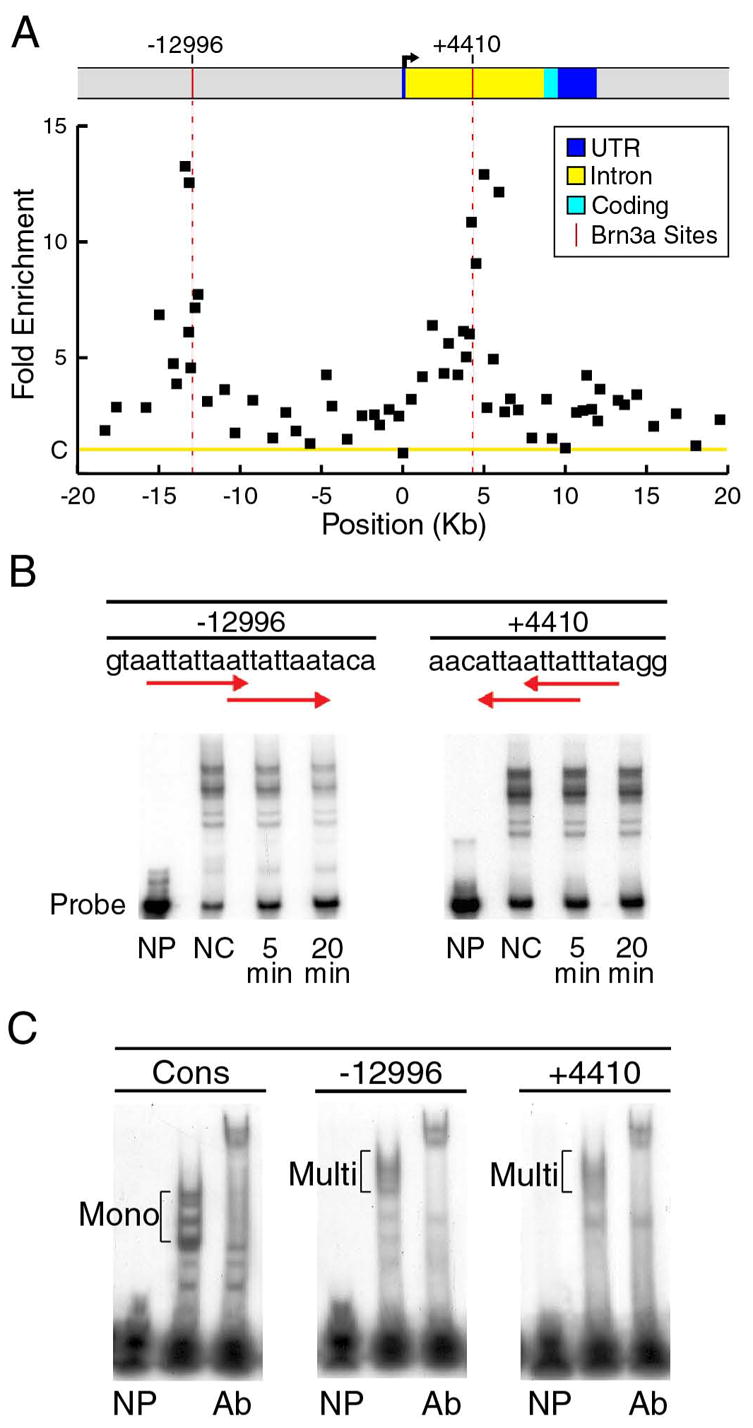
(A) ChIP analysis of Brn3a binding to the NeuroD4 locus in E13.5 ganglia. Sixty-three primer pairs were used in real-time PCR assays to screen the locus from −20kb to +20kb relative to the transcriptional start site (Table S3). The fold enrichment of the selected versus unselected chromatin was normalized to a control value of one (C on Y-axis), based on the signal the Alb-1 locus (Materials and Methods). The average enrichment from three selection experiments using independent pools of ganglia is shown for each primer pair. Sequence analysis of the regions of maximum ChIP selection revealed consensus Brn3a binding sites at −12996 and +4410 relative to the start of transcription (vertical red lines). Differences between the ChIP selection peaks at −12996 and +4410 and Alb-1 locus control values were highly significant (p=0.003 and p=0.002, respectively, Materials and Methods).
(B) Kinetic EMSA assays were used to determine the relative stability of Brn3a binding to the sites identified by ChIP. In these assays, Brn3a protein was allowed to bind radiolabeled oligonucleotides, and the complexes were then incubated in the presence of an excess of specific competitor oligonucleotide (Materials and Methods). The amount of complex remaining after 5 and 20 minutes was used to determine the half-life of each complex. The relative first-order dissociation rates of the Brn3a-DNA complexes observed in these assays allow a rapid approximate comparison of relative site affinity (Gruber et al., 1997; Trieu et al., 1999). Multiple complexes were observed due to size heterogeneity of the expressed protein and multimeric binding to overlapping recognition sites (arrows). NP, no Brn3a protein; NC, no competitor; 5 min, 5 minute incubation with competitor, 20 min, 20 minute incubation with competitor.
(C) Oligonucleotide probes containing a previously determined optimal monomeric consensus binding site (Cons, Gruber et al., 1997) and the Brn3a recognition sequences in the NeuroD4 locus were used to demonstrate the interaction of multimeric binding of Brn3a to the NeuroD4 sites. Supershifts with Brn3a antibody (Ab) demonstrate that all major complexes contain Brn3a. NP, no Brn3a protein; B3, Brn3a protein containing cell lysate added; Ab, cell lysate plus Brn3a antiserum; Mono, monomeric Brn3a complexes; Multi, multimeric Brn3a complexes.
