Figure 5. Markers of chromatin modification at the Pou4f1 locus.
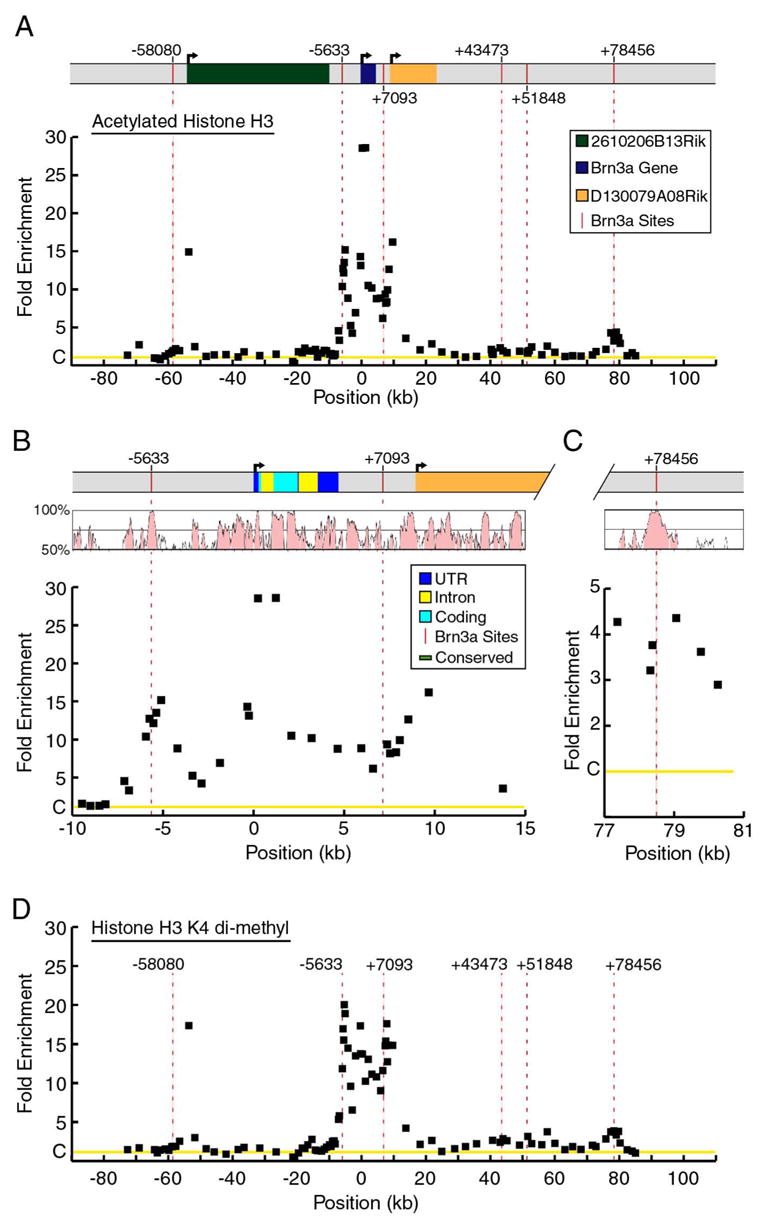
(A) Locus-ChIP assays were performed for acetylated histone H3 over a ~160 kb region encompassing the Pou4f1 locus in E13.5 trigeminal ganglia. Data show average enrichment from two sets of assays using separate pools of ganglia. H3 acetylation is increased within a ~15 kb region including the autoregulatory domain, transcriptional start site and primary transcript. The area of enrichment at −53,620 is closely associated with the transcription start site of an adjacent gene, 2610206B13Rik, and does not coincide with the Brn3a binding site at −58,080 (vertical red bar, dashed line). The fold enrichment of the selected versus unselected chromatin was normalized to a control value of one (C on Y-axis), based on the signal from the Alb-1 locus (Materials and Methods).
(B) Detailed map of histone H3 acetylation within a 25 kb region containing the Pou4f1 transcription unit. A region of increased acetylation encompasses the Brn3a autoregulatory site cluster at −5,633, the transcription start site, and extends beyond the 3′ end of the transcript to include the Brn3a binding site at +7,093. A VISTA plot of mouse-human homology within the locus indicates that regions of enhanced acetylation are correlated with areas of conserved sequence.
(C) Detailed map of histone-H3 acetylation from a 4 kb region containing the in vivo Brn3a binding site at +78,456. The region of moderately enhanced acetylation associated with this site also shows sequence conservation between the mouse and human genomes.
(D) Locus-ChIP of the Pou4f1 locus using antibodies to dimethylated H3–K4. The patterns of H3 acetylation and H3–K4 dimethylation are highly congruent.
