Figure 1.
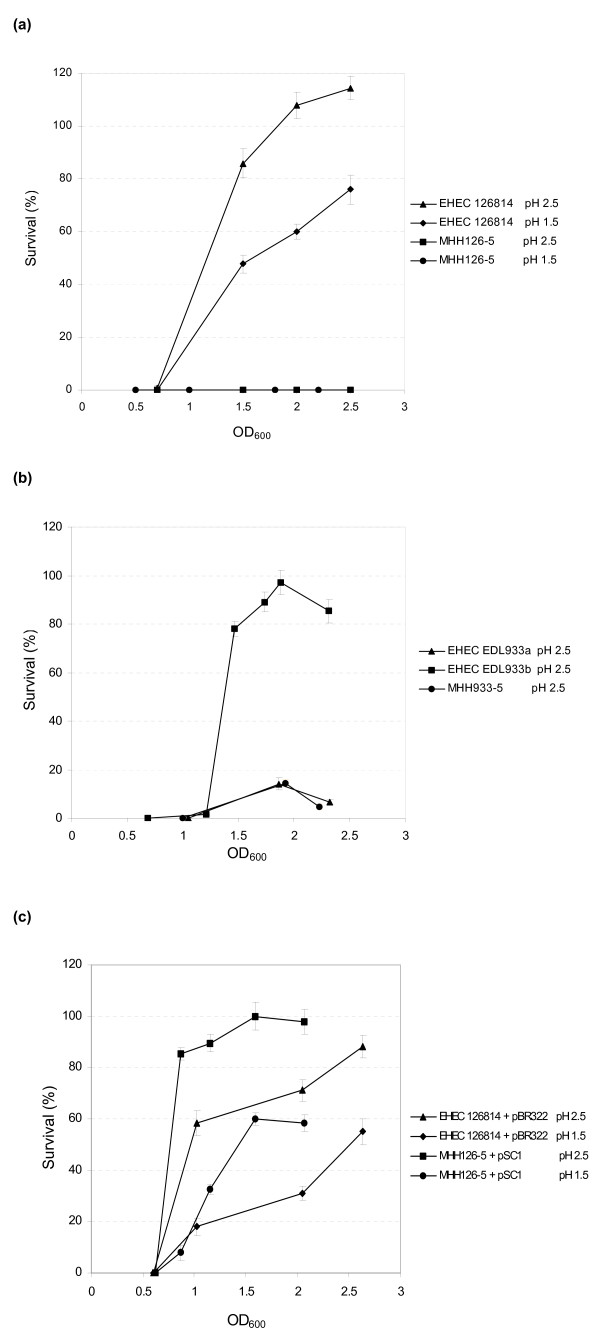
A: Acid resistance of EHEC 126814 and E. coli MHH126-5. Inducible acid resistance of EHEC wild type strain 126814 and its isogenic rpoS deletion mutant E. coli MHH126-5 was investigated after 2 h incubation in LB media at pH 2.5 or 1.5. The wild type strain showed a high level of acid resistance, which was induced from OD600 0.7 of the preparatory culture. It reached up to 115 % survival at OD600 2.5 of the starter culture, indicating that EHEC 126814 was able to grow under these conditions. In LB media with pH 1.5 up to 75 % of the inoculum survived. E. coli MHH126-5 was completely sensitive to acid treatment regardless of pH and OD600 of the preparatory culture. Percentage survival figures in relation to OD600 of one typical experiment are depicted. The means and standard deviations were calculated from three independent dilution series made at each individual measuring point. B: Acid resistance of EHEC EDL933a, EDL933b and E. coli MHH933-5. EHEC EDL933b was very acid resistant in all experiments. However, between EHEC wild type strain EDL933a and its mutant E. coli MHH933-5 no differences could be observed. Both isolates showed weak resistance under acidic growth conditions and showed a similar behavior in all other experiments. In contrast to EHEC 126814, acid resistance of the O157 isolates was induced at OD600 1.2 of the starter culture. One typical experiment has been shown as a representation of all independent tests carried out. The means and standard deviations were calculated from three independent dilution series prepared at each individual measuring point. C: Acid resistance of E. coli MHH126-5 complemented with pSC1. This figure depicts the inducible acid resistance in relation to OD600 of one typical experiment. Acid resistance was assayed at pH 2.5 and 1.5. By complementation of rpoS deletion mutant E. coli MHH126-5 with pSC1, containing its own rpoS gene cloned into plasmid pBR322, a phenotype could be restored that was even more resistant to acid stress than wild type strain EHEC 126814. OD600 of acid resistance induction was identical to values obtained with the wild type strain, shown in figure 1A. In order to compare growth conditions in LB media containing ampicillin, positive control EHEC 126814 had been transformed with plasmid pBR322. Compared to figure 1A, the antibiotic and/or pBR322 negatively influenced acid resistance of this strain. The percentage survival at pH 2.5 was below 90 %. One typical experiment is shown representative of independent tests. The means and standard deviations were calculated from three independent dilution series made at each individual measuring point.
