Figure 5. .
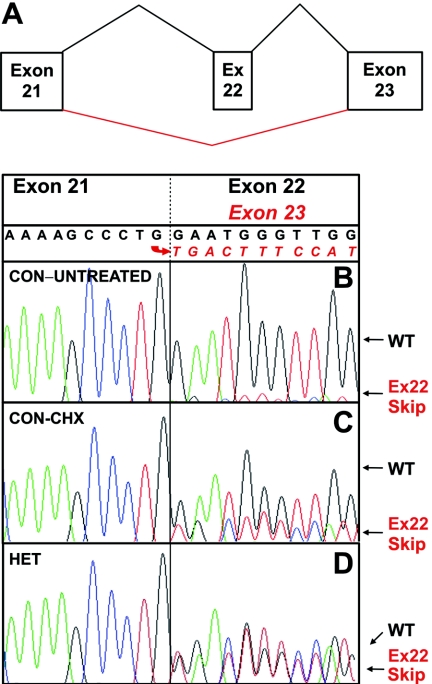
Exon 22 splicing. A, Schematic depiction of the splicing patterns resulting from exon 22 retention or skipping. B, cDNA sequencing in an LCL from a normal control (CON), showing predominance of exon 22 sequence following that of exon 21 but also low levels of underlying sequence readable as exon 23. C, Treatment of the same LCL from a normal control with CHX for 4 h before cDNA synthesis, which increases the relative level of sequence with exon 22 skipping. D, cDNA sequencing in an LCL from a compound heterozygote (HET) for splice-acceptor mutation in intron 21, c.1948-16T→G (patient 9), which shows comparable levels of inclusion and exclusion of exon 22 sequence following that of exon 21. Ex=exon; WT=wild type.