Figure 3.
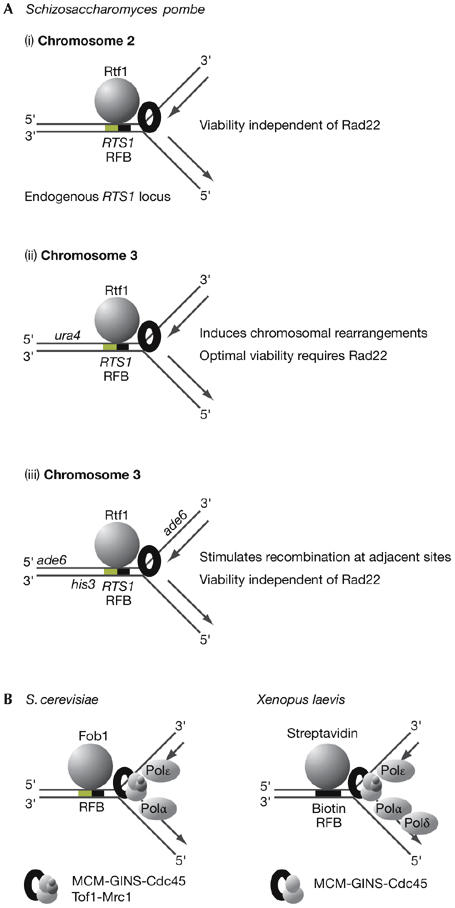
Pausing of forks at eukaryotic replication fork barriers. (A) Pausing of forks at the replication termination sequence 1 (RTS1) barrier in Schizosaccharomyces pombe can have different outcomes depending on the chromosomal context (for (ii) see Lambert et al, 2005; for (iii) see Ahn et al, 2005). (B) Chromatin immunoprecipitation studies have shown that replisome components persist at paused forks in Saccharomyces cerevisiae (see Calzada et al, 2005) and Xenopus laevis (see Pacek et al, 2006). Fob1, fork blocking 1; Pol, DNA polymerase; Rtf1, replication termination factor 1. The MCM (mini-chromosome maintenance) helicase is required for the progression of eukaryotic DNA replication forks, together with the Cdc45 protein and the four-protein GINS complex (Sld5–Psf1–Psf2–Psf3). In budding yeast, MCM–GINS–Cdc45 also interact with the regulatory proteins Tof1 and Mrc1.
