Figure 3.
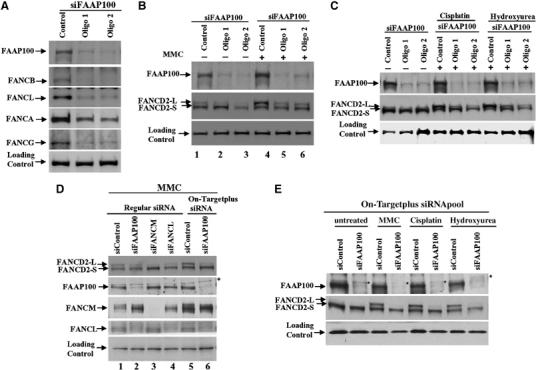
FAAP100 is essential for FANCD2 monoubiquitination and the stability of the FA core complex. (A) Immunoblotting shows that HeLa cells depleted of FAAP100 by two different siRNA oligos not only have reduced levels of FAAP100, but also of several other FA core complex components, including FANCB, FANCL, FANCA, and FANCG. HeLa cells transfected with a scrambled siRNA oligo are shown as control. The image of FAAP100 depletion (top panel) was reproduced from the lanes 1–3 of the top panel in (B), to allow easy comparison of the reduction of FAAP100 protein level with those of other FA proteins. (B, C) Immunoblotting shows that HeLa cells depleted of FAAP100 display reduced level of monoubiquitinated FANCD2 in cells that are either untreated (−), or treated with mitomycin C (MMC), cisplatin, or hydroxyurea (+). The monoubiquitinated and non-ubiquitinated FANCD2 proteins are indicated by FANCD2-L and FANCD2-S, respectively. (D) Immunoblotting shows that HeLa cells depleted of FAAP100 by On-Targetplus SMARTpool siRNAs display a level of monoubiquitinated FANCD2 comparable to cells depleted of FANCM or FANCL (compare the relative ratio between FANCD2-L and FANCD2-S in lane 6 with those in lanes 3 and 4). In addition, cells depleted by On-Target siRNAs have lower levels of FAAP100 and monoubiquitinated FANCD2 (compare lane 6 with lane 2). A nonspecific polypeptide was marked with an asterisk, which was resolved from FAAP100 using a 6% SDS gel. (E) Immunoblotting shows that HeLa cells depleted of FAAP100 by On-Targetplus SMARTpool siRNAs (siFAAP100) reduced monoubiquitination of FANCD2 in the presence of several DNA-damaging drugs. Note that the FAAP100 level in depleted cells is similar that of a nonspecific polypeptide (marked by an asterisk), indicating that its level is very low and close to the detection limit of the antibody. The cell lysis buffer in (A), (B) and (C) includes 8 M urea, which allows more efficient extraction of FANCD2-L and FANCB. The cell lysis buffer in (D) and (E), and those used in previous studies of FANCL, FANCB, and FANCM, do not include urea. Thus, the results in (D) and (E) should be more suitable for comparison with the previous studies.
