Figure 1.
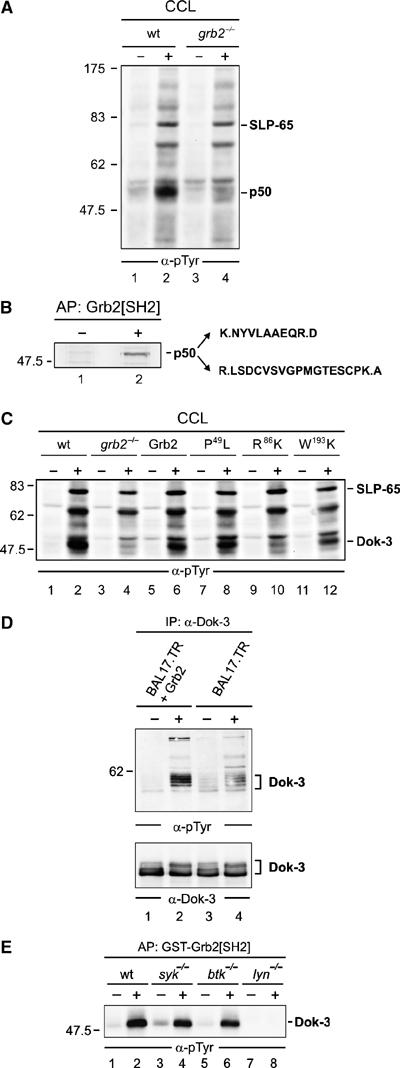
Grb2 controls Lyn-mediated phosphorylation of the adaptor protein Dok-3. (A) Wild-type (wt) and Grb2-deficient (grb2−/−) DT40 cells (lanes 1, 2 and 3, 4) were left untreated (−) or stimulated through their BCRs for 3 min (+). Equal amounts of proteins from cleared cellular lysates (CCL) were analyzed by anti-phosphotyrosine (α-pTyr) immunoblotting. (B) The major phosphotyrosine-containing protein, p50, was affinity-purified (AP) by GST-Grb2[SH2] from stimulated DT40 cells (lane 2), silver-stained, excised, digested by trypsine and peptide products were analyzed by ESI-Trap mass spectrometry. Purified proteins from unstimulated cells served as negative control (lane 1). The obtained amino-acid sequences are shown (single-letter code) with lysine (K) and arginine (R) being inferred from trypsine cleavage specificity (indicated by dots). These sequences matched a partial chicken EST (GenBank accession number XP_427516). Full-length chicken cDNA was isolated and submitted to GenBank with the accession number EF051736 (see also Supplementary Figure S1). (C) Wild-type (lanes 1 and 2) and grb2−/− DT40 cells (lanes 3 and 4) reconstituted with either wild-type Grb2 (lanes 5 and 6) or Grb2 variants, in which one of the three SH domains has been inactivated by single amino-acid substitution (N-terminal SH3 domain, P49L; SH2 domain, R86K; C-terminal SH3 domain, W193K; lanes 7–12), were left untreated (−) or stimulated through their BCRs (+). Equal amounts of proteins from CCL were subjected to anti-pTyr immunoblotting. To confirm equal loading, phospho-SLP-65 was detected separately by anti-SLP-65 immunoblotting (data not shown). (D) Murine Bal17.TR B cells, deficient for Grb2 expression, were transfected with an expression vector for Grb2 (lanes 1 and 2) or the empty vector as control (lanes 3 and 4) and left untreated (−) or stimulated through their BCRs (+). CCL were subjected to anti-Dok-3 immunoprecipitation and purified proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies to pTyr and Dok-3 (upper and lower panels, respectively). (E) Resting (−) or BCR-activated (+) wild-type DT40 cells (lanes 1 and 2) or variants deficient for the protein tyrosine kinase Syk (lanes 3 and 4), Btk (lanes 5 and 6) or Lyn (lanes 7 and 8) were lysed and subjected to affinity purification with GST-Grb2[SH2]. Phosphorylated Dok-3 was detected by anti-pTyr immunoblotting. Relative molecular masses of marker proteins are indicated on the left in kDa.
