Figure 1.
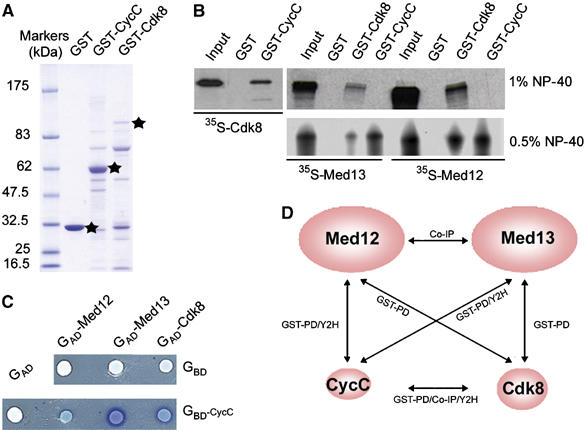
Drosophila Med12 and Med13 interact with Cdk8 and/or CycC in vitro and in a yeast two-hybrid assay. (A) Coomassie staining of purified recombinant GST-Cdk8 and GST-CycC fusions. Full-length forms are indicated by asterisks. (B) GST pull-down interactions between Cdk8, CycC, Med12 and Med13. 35S-labeled Med12 or Med13 produced in vitro was incubated under two distinct conditions (1 or 0.5% NP-40) with GS-bound GST, GST-CycC or GST-Cdk8 (shown in panel A). Input (10%) and retained proteins were resolved by SDS–PAGE and detected by fluorography. (C) CycC interacts with Cdk8, Med12 or Med13 in a yeast two-hybrid assay. Interactions of CycC with Med12, Med13 or Cdk8 were revealed using an X-gal overlay assay as described in Werner et al (1993). Empty pAS2 vector (GBD) or expressing a GBD-CycC fusion was tested against empty pACT2 vector (GAD) or expressing GAD-Med12, GAD-Med13 or GAD-Cdk8 fusions as indicated. (D) Pairwise interactions between Drosophila Cdk8 module subunits, as detected from GST pull-down (GST-PD), yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) and/or co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) experiments. Co-IP data are from Leclerc et al (1996) and Janody et al (2003).
