Figure 1.
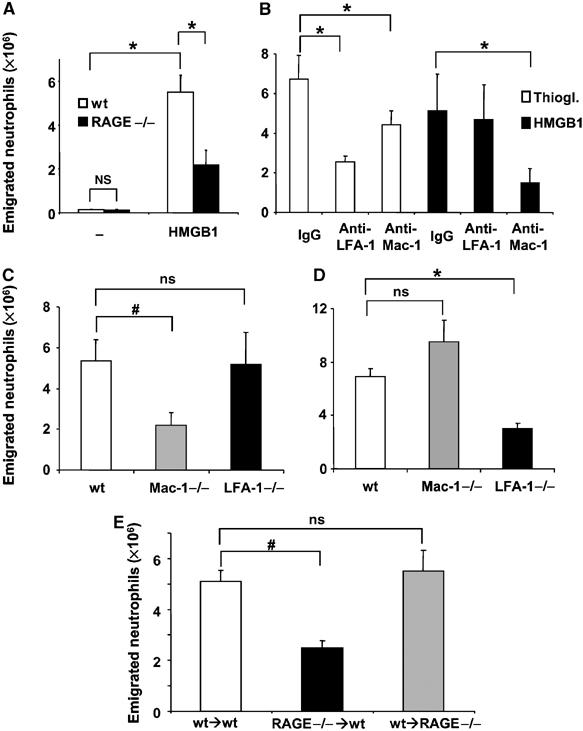
HMGB1-mediated inflammatory cell recruitment in vivo. (A) The number of neutrophils in wild-type (open bars) or RAGE−/− (filled bars) mice is shown 4 h after the i.p. injection of buffer (−) or HMGB1 (10 μg). (B) Sixty minutes before thioglycollate (open bars) or HMGB1 (filled bars) administration, wild-type mice were treated with isotype control mAb, with a blocking mAb against LFA-1 or with a blocking mAb against Mac-1 (each 100 μg). (C) HMGB1 induced peritonitis in wild-type, Mac-1−/−, and LFA-1−/− mice. (D) Thioglycollate induced peritonitis in wild-type, Mac-1−/−, and LFA-1−/− mice. (E) HMGB1 induced peritonitis in sublethally irradiated wild-type mice reconstituted with bone marrow cells from wild-type mice (wt → wt), sublethally irradiated wild-type mice reconstituted with bone marrow cells from RAGE−/− mice (RAGE−/− → wt) and sublethally irradiated RAGE−/−mice reconstituted with bone marrow cells from wild type (wt → RAGE−/−). Data are expressed as absolute numbers of emigrated neutrophils into the peritoneum. *P<0.01; #P<0.05; ns: not significant. Data are mean±s.d. (n=3–6 mice/group).
