Figure 4.
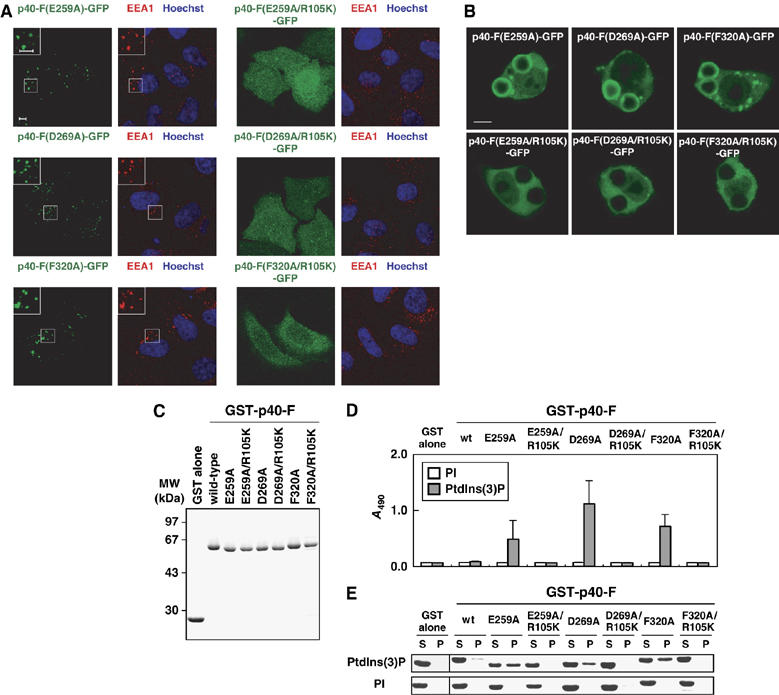
Role of E259, D269, and F320, residues in the PB1 interface for the PX domain, in the PtdIns(3)P-binding activity. (A) Subcellular distribution of p40phox and its mutant proteins carrying the indicated amino-acid substitution in transiently transfected HeLa cells. Left panel, distribution of GFP-tagged p40phox in fixed HeLa cells (green); right panel, distribution of endogenous EEA-1 (red) and Hoechst staining of the nucleus (blue) in the same field of fixed HeLa cells. The insets show the magnified views. Scale bar, 5 μm. (B) Localization of ectopically expressed p40phox and its mutant proteins in RAW264.7 cells ingesting IgG-coated beads. Scale bar, 5 μm. (C) SDS–PAGE analysis of GST-tagged p40phox and its mutant proteins carrying the indicated amino-acid substitution, which were used in the following lipid-binding assays (D, E). (D) The PtdIns(3)P-binding activity estimated by the ELISA-format phosphoinositide-binding assay as in Figure 1E. (E) The PtdIns(3)P-binding activity estimated by the liposome co-sedimentation assay as in Figure 1F.
