Figure 3.
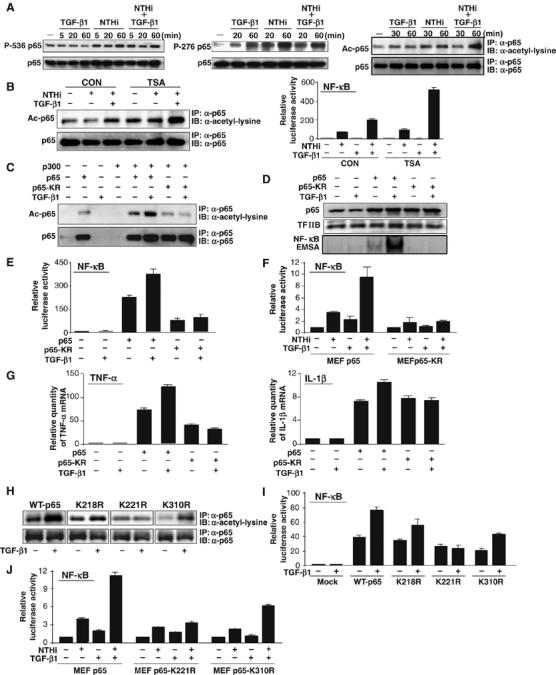
TGF-β1 synergistically enhances NTHi-induced NF-κB activation via induction of p65 acetylation at lysine 221. (A) Synergistic enhancement of p65 acetylation was observed in HeLa cells treated with both NTHi and TGF-β1 (1 ng/ml; right panel), whereas TGF-β1 induced p65 phosphorylation at Ser276 but not Ser536 (left and middle panels). Acetylation of p65 was detected by immunoblotting (IB) of the anti-p65 (α-p65) immunoprecipitates (IP) with anti-acetylated lysine antibodies. Levels of p65 present in each of the lysates are shown in the lower panel. (B) TSA enhanced NTHi-induced p65 acetylation and NF-κB activation. (C) TGF-β1 enhanced p65 acetylation induced by coexpressing WT p300 with WT p65, but not with p65-KR mutant (lysine 218/lysine 221/lysine 310 acetylation site mutant) in HeLa cells. (D) TGF-β1 enhanced DNA-binding activity of NF-κB in HeLa cells transfected with WT p65 but not with p65-KR mutant. (E) TGF-β1 enhanced NF-κB activation in HeLa cells transfected with WT p65 but not with p65-KR mutant. (F) TGF-β1 enhanced NTHi-induced NF-κB activation in p65−/− MEFs reconstituted with WT p65 but not in p65-KR-reconstituted p65−/− MEFs. (G) TGF-β1 enhanced TNF-α and IL-1β expression in HeLa cells transfected with WT p65 but not with p65-KR. (H) Mutation of lysine 221, but not 218 or 310, markedly decreased p65 acetylation in response to TGF-β compared to WT p65. (I) TGF-β1 enhanced NF-κB-dependent transcriptional activity in cells transfected with p65-K218R and p65-K310R, but not with p65-K221R mutant compared to cells transfected with WT p65. (J) Synergistic NF-κB activation was observed in p65-K310R-reconstituted MEFs but not in p65-K221R-reconstituted MEFs in response to NTHi and TGF-β1 compared to p65−/− MEFs reconstituted with WT p65. Values are means±s.d. (n=3). Data are representative of three or more independent experiments.
