Figure 1.
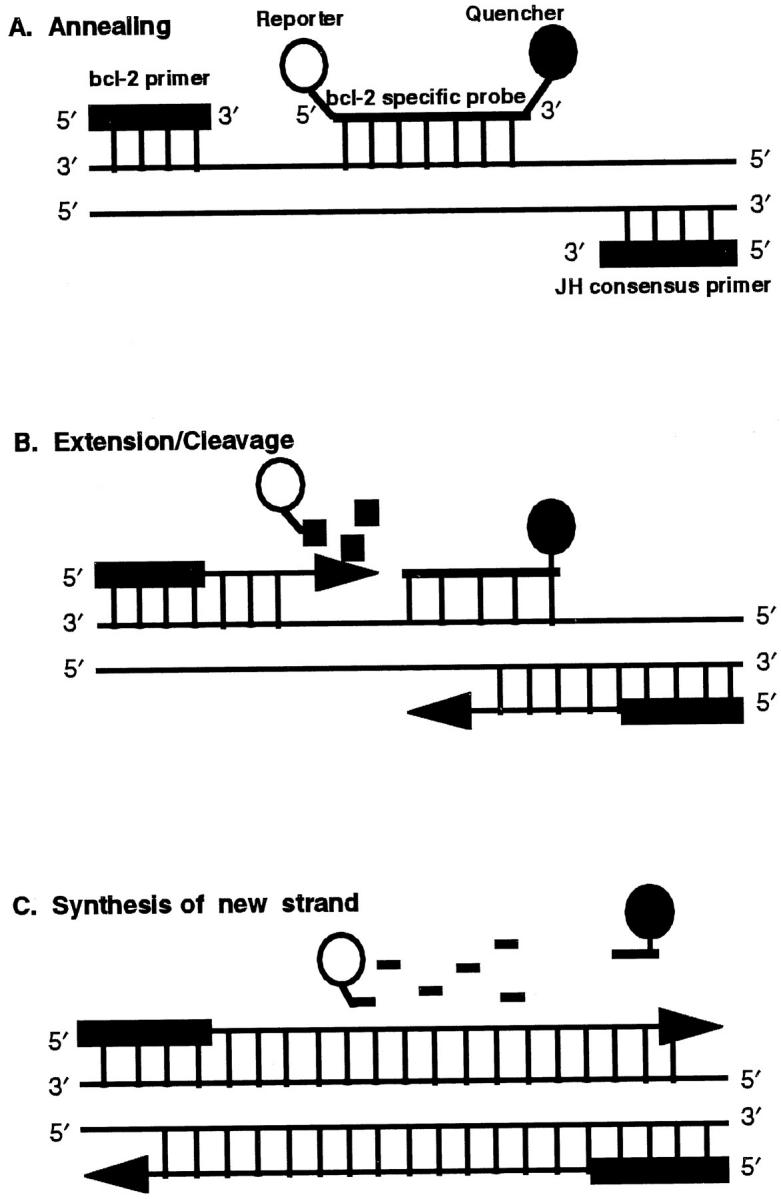
Schematic of sequence-specific annealing and 5′–3′ exonuclease-based cleavage of the fluorescent dye-labeled probe. A: Annealing of the primers and the probe to the target sequence. The probe is labeled with a reporter dye, 6-carboxy fluorescein, at the 5′ end and a quencher dye, 6-carboxy-tetramethyl rhodamine, at the 3′ end. When both dyes are attached to the probe, fluorescence emission of the reporter dye is quenched by the quencher dye. B: Extension of the primer and the initiation of cleavage of the probe at its 5′ end by Taq polymerase. C: Release of the probe from the target strand and completion of the new strand synthesis. The separation of the reporter dye from the quencher dye abrogates the quencher effect and results in an increase in the fluorescence signal of the reporter dye.
