Figure 5.
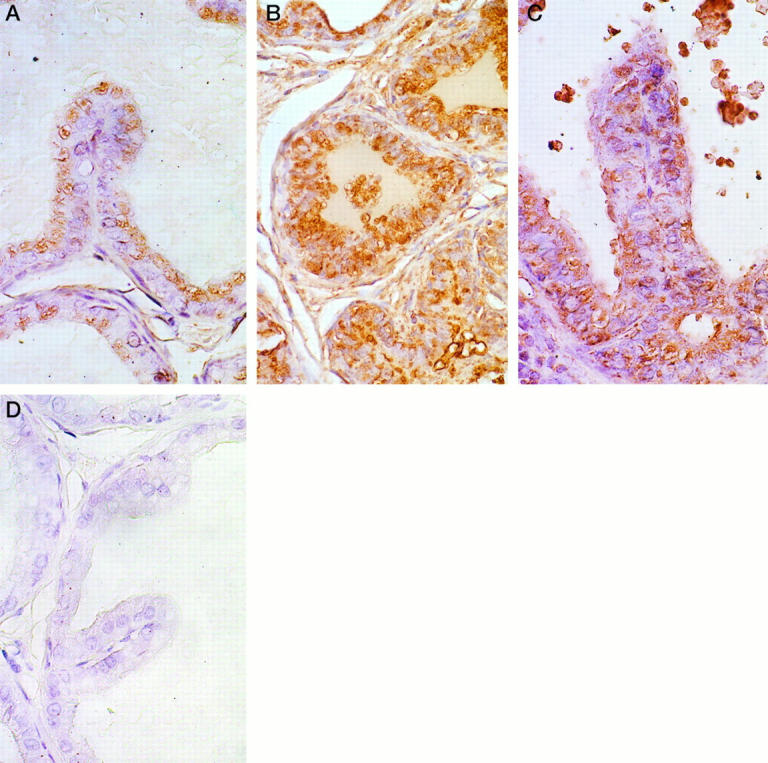
Immunohistological detection of clusterin expression in prostatic epithelia. A: Clusterin immunostaining in the DLP of an intact, untreated rat. Light positive immunostaining is present within apical vacuoles of secretory cells. Magnification, ×420. B: Clusterin immunostaining in the DLP of a rat castrated for 7 days. Note the intense expression of clusterin in the atrophic acinar lining cells. Although not strikingly evident in this photomicrograph, positive staining was also evident in stromal cells in the DLPs of castrated rats. Magnification, ×160. C: Clusterin immunostaining in a dysplastic lesion in the DLP of a rat treated with T+E2 for 16 weeks. Strong immunostaining is evident in this lesion. Clusterin expression in this dysplastic acinus is comparable to that observed in the regressing ducts/acini of the castrated rat (illustrated in B). Within any DLP section from a T+E2-treated rat, expression of clusterin was always stronger in dysplastic foci than in unaltered glands. Magnification, ×500. D: Omission negative control. No immunostaining was detected in this section of DLP from an intact rat. The same negative results were observed in omission controls from the VPs and DLPs of castrated and T+E2-treated rats. Magnification, ×500. All sections were counterstained with Harris hematoxylin.
