Figure 1.
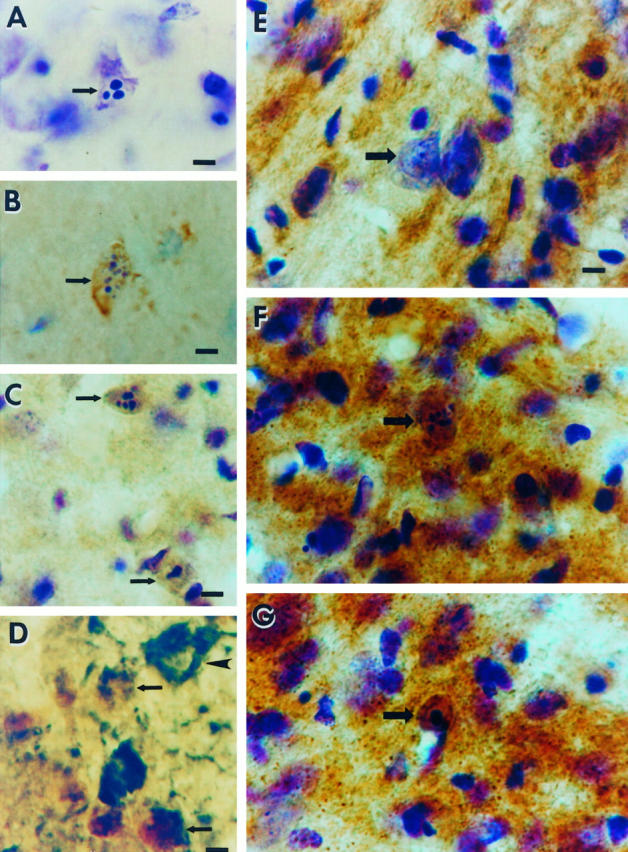
Occipital cortex ablation in the adult rat results in apoptosis of geniculocortical projection neurons within the dLGN that is associated with oxidative damage to the nucleus and increased mitochondrial COX activity within the perikaryon. A: Cresyl violet staining shows a representative apoptotic neuron (arrow) within the dLGN at 6 days postlesion. Note the three round clumps of chromatin within the nucleus, consistent with the morphology of apoptosis. The identification of these cells as neurons has been described. 12 Scale bar = 10 μm. B: Immunoreactivity (brown labeling) for the oxidative stress marker, OH8dG, is detected within apoptotic neurons (arrow) at 5 days postlesion. The cresyl violet counterstaining (purple) shows that this cell (arrow) is in the early stages of apoptotic chromatin condensation, as indicated by the formation of numerous, small aggregates of chromatin, and has not yet undergone shrinkage of the cell body (compare the size of the neuron in B with that of the apoptotic neurons in C). Scale bar = 10 μm. C: At 7 days postlesion, apoptotic neurons (arrows) show intense OH8dG immunoreactivity (brown) throughout the nucleus. The cresyl violet counterstaining (purple) reveals that these neurons are in the late stages of apoptosis, as indicated by the chromatin clumping and the cellular shrinkage. Scale bar = 10 μm. D: Double label immunodetection of OH8dG (brown) and the retrograde tracer FG (dark green) demonstrates that the cells that have evidence for oxidative stress within the nucleus are geniculocortical projection neurons (arrows), whereas a nearby undamaged geniculocortical projection neuron (arrowhead) has no OH8dG immunoreactivity within the nucleus and is not shrunken. Scale bar = 10 μm. E: In COX histochemical preparations counterstained with cresyl violet, COX activity (brown) in the control (contralateral to the occipital cortex ablation) dLGN is localized within the neuropil, and only faint activity appears within neuronal cell bodies (arrow). Scale bar = 10 μm (applies also to F and G). F and G: In the dLGN ipsilateral to the occipital cortex ablation, COX histochemistry/cresyl violet staining shows that axotomized neurons (arrows) at early stages of apoptosis at 5 days (F) and later stages of apoptosis at 6 days (G) postlesion are highly enriched in COX activity, indicating the accumulation of functional mitochondria within the perikaryon.
