Figure 1.
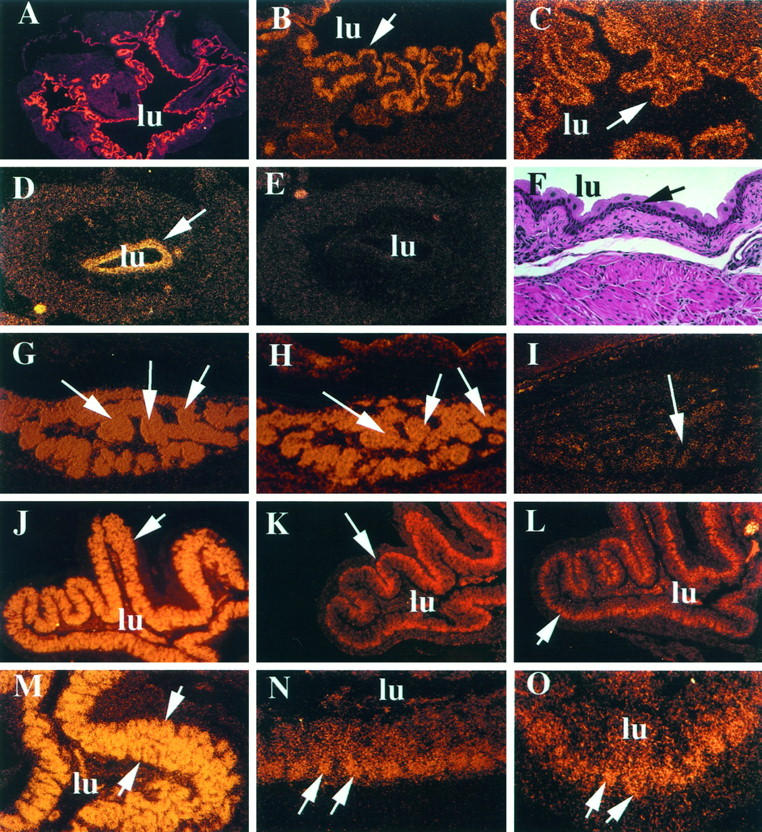
Differential expression of PPARγ, PBP, and mSRC-1 mRNAs in bladder, brown fat, and colon by in situ hybridization. A to F: Expression of PPARγ and PBP in bladder. A and B: Expression of PPARγ in adult mouse bladder transitional epithelium at low (×5) and high (×20) power, respectively. C: Expression of PBP in the adult bladder transitional epithelium. D and E: antisense and sense panels, respectively, for PPARγ expression in the urogenital sinus of a stage E15.5 mouse. F: Hematoxylin and eosin-stained adult urinary bladder for histological reference. A to F, arrows: Transitional epithelium; lu, lumen of the bladder. G and H: High PPARγ and PBP expression in the E15.5 brown fat (arrows), respectively. I: Sense control for PPARγ showing background signal levels compared with G. J to O: Expression of PPARγ, PBP, and SRC-1 in the adult colon. J to L: Photographs taken at low power (×5). M to O: Photographs taken at high power (×20). J and M denote PPARγ expression (J, arrows, colonic villi; M, arrows, entire villus), K and N denote PBP expression, and L and O denote SRC-1 expression. The arrows in K, L, N, and O point to the crypts of the villus. In J to O, lu denotes the lumen of the colon.
