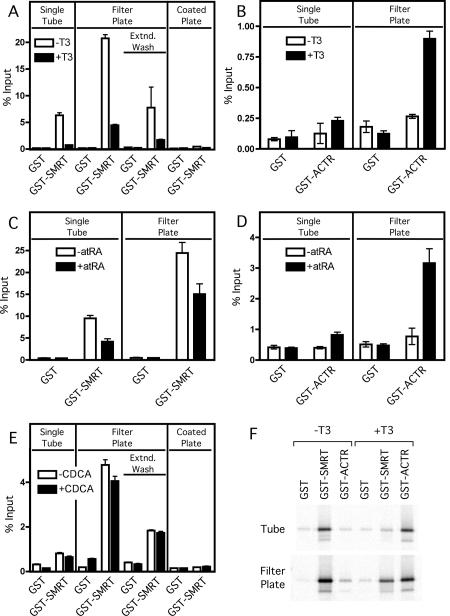
Figure 1. Comparison of GST-pulldown methodologies: microfuge tube versus filter-plate protocols.
Non-recombinant GST, GST-SMRTτ (amino acids 2077-2471; A, C, E and F), or GST-ACTR (amino acids 621-821; B, D, and F) bound to glutathione agarose were incubated with in vitro translated 35S-methionine radiolabeled TRα1 (A, B and F), RARα (C and D), or FXR (E) protein in either the absence (open bars) or presence (filled bars) of cognate agonist (1 µM T3 for TRα1, 1µM ATRA for RARα or 100 µM CDCA for FXR). Samples were bound, washed, and eluted with free reduced glutathione using the conventional individual tube assay (“Single Tube”), the modified filter microplate assay (“Filter Plate”), or the glutathione coated Reacti-Bind plate assay (“Coated Plate”). Extended wash filter microplate samples (“Extnd. Wash”) were incubated 15 min between washes. Samples were resolved on a SDS-10% PAGE gel prior to fixing, staining and scanning of the dried gel with a Molecular Dynamics Storm 840 Phosphorimager. Quantification of the radiolabeled bands was performed using ImageQuant software version 4.2. Assays were performed in triplicate; error bars indicate standard deviation. (F) Representative Phosphorimager gel images used for analysis in panels A and B.