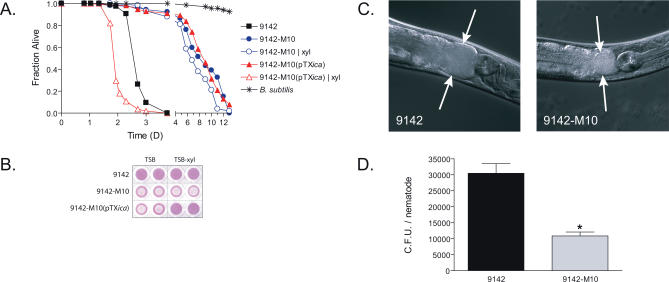
Figure 3. S. epidermidis Virulence in the C. elegans Infection Model Depends on icaADBC .
(A) Survival of C. elegans infected with S. epidermidis strain 9142-M10 (circles), which contains a transposon insertion in the icaA gene, and the complemented strain 9142-M10(pTXica) (triangles), which carries the icaADBC operon driven by the xylose-inducible PxylA promoter, compared to wild-type S. epidermidis 9142 (squares) and B. subtilis (asterisks). Survival assays were performed under standard conditions (closed symbols) or using plates supplemented with 2% xylose (xyl, open symbols).
(B) Biofilm formation of S. epidermidis 9142, 9142-M10, and 9142-M10(pTXica) on polystyrene. Attachment to polystyrene 96-well flat bottom microtiter plate was performed as described in the Materials and Methods. Strains were grown in TS broth without supplementation (TSB) or supplemented with 2% xylose (TSB-xyl).
(C) Nomarski micrograph of C. elegans after feeding for 24 h on S. epidermidis 9142 or 9142-M10. Arrows demarcate the intestinal tract lumen. Magnification, ×40.
(D) Quantification of intestinal bacteria obtained by disruption of worms after 24 h of feeding on either S. epidermidis 9142 or 9142-M10. Values represent the mean of five samples with approximately eight worms per sample ± standard error of the mean (SEM). The asterisk indicates a significant difference (p < 0.001).