Fig. 2.
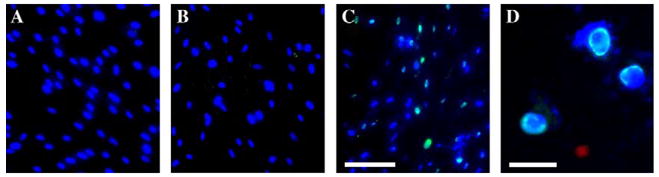
PEI-based delivery of anti-lamin antibody into cultured human fibroblasts. Fibroblast nuclei in cell culture were visualized using DAPI (blue fluorescence). Antibody to lamin was detected using secondary biotinylated antibody and streptavidin–FITC (green fluorescence). (A) Incubation (24 h) with antibody to lamin without PEI. (B) Incubation (24 h) with PEI (3 μg/ml) without antibody. (C) Incubation (24 h) with PEI–antibody complexes. Images show delivery of anti-lamin antibody by PEI into human fibroblasts. Note antibody signal detected exclusively in the area of lamin localization in cell nuclei. Only part of cells (~one-fourth of all cell nuclei) are stained, and the signal is of uneven intensity, indicating different numbers of antibody molecules per cell. Bar = 50 μm. (D) High-magnification image of cells after 24 h incubation with PEI–antibody complexes. Note precise antibody staining of the nuclear envelope. Bar = 20 μm.
