Abstract
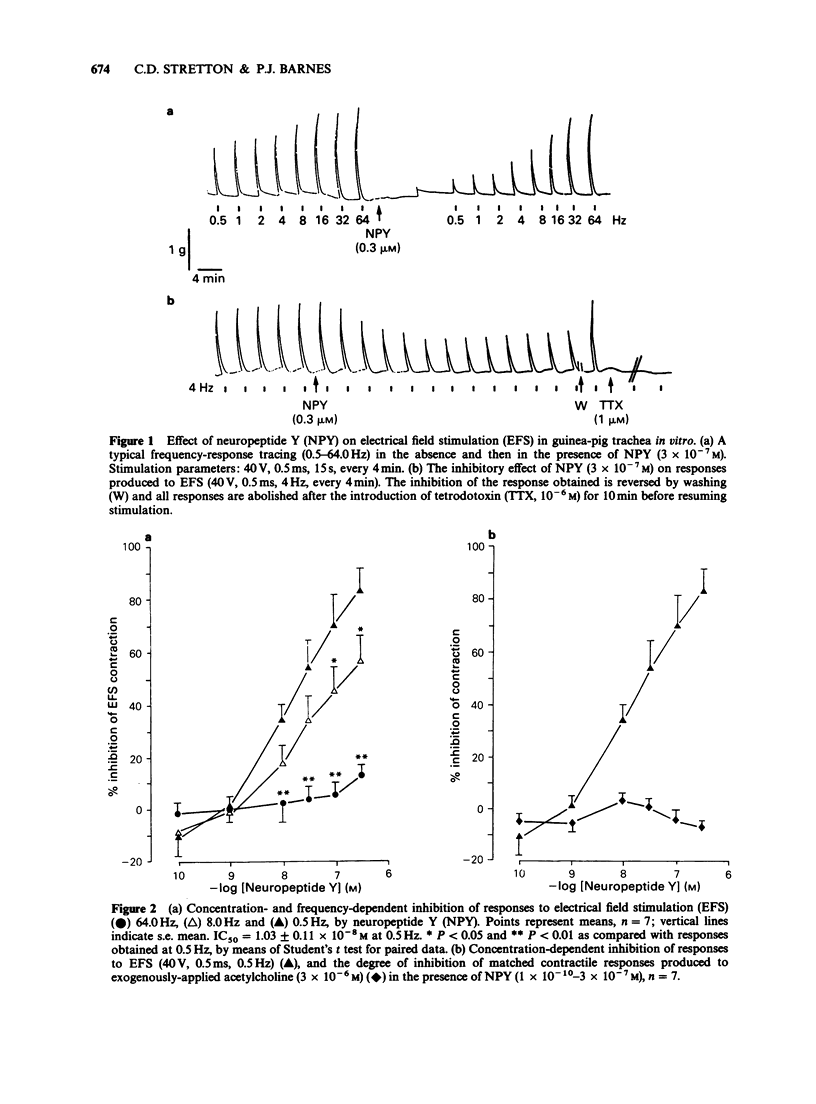
1. Neuropeptide Y (NPY) is localized to adrenergic nerves in guinea-pig airways but its function is not known. 2. NPY (1 X 10(-10)-3 X 10(-7) M) had no direct effect on guinea-pig tracheal smooth muscle in vitro. 3. NPY produced a concentration- and frequency-dependent inhibition of the cholinergic component of responses elicited by electrical field stimulation (EFS) whilst having no effect on the contractile response to exogenously applied acetylcholine (ACh). 4. Yohimbine was able to reverse significantly the inhibitory effect of noradrenaline on the cholinergic component to EFS without having any significant effect on the inhibition produced by NPY. 5. Neither blockade of beta-adrenoceptors by propranolol, nor depletion of adrenergic nerves by incubation with 6-hydroxydopamine caused any significant alteration in the response to EFS in the presence of 3 X 10(-7) M NPY. Bretylium tosylate incubation to prevent noradrenaline release produced a small but significant enhancement of the inhibitory effect of NPY on EFS at high frequencies. 6. NPY appears to reduce the cholinergic component to EFS via a prejunctional mechanism, acting directly on receptors on cholinergic nerve terminals, rather than affecting adrenergic mechanisms. NPY released by adrenergic nerves may modulate cholinergic neurotransmission in guinea-pig airways.
Full text
PDF

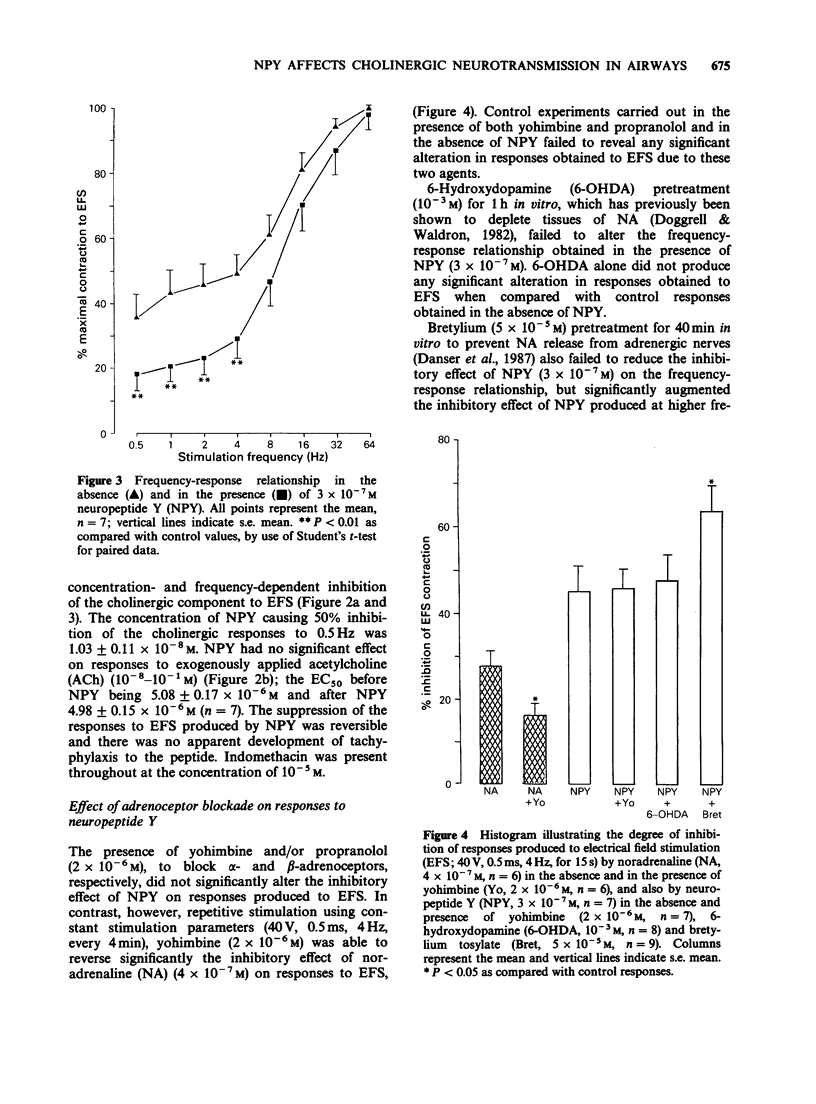
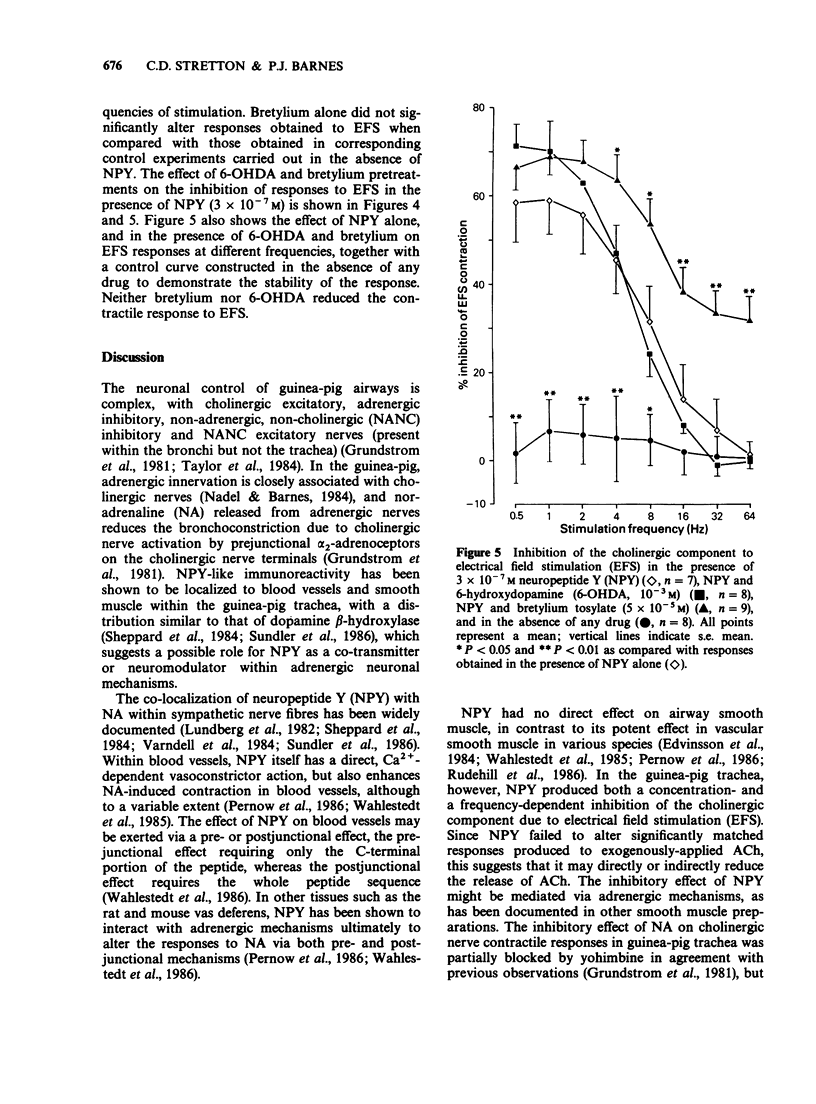


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agnati L. F., Fuxe K., Benfenati F., Battistini N., Härfstrand A., Tatemoto K., Hökfelt T., Mutt V. Neuropeptide Y in vitro selectivity increases the number of alpha 2-adrenergic binding sites in membranes of the medulla oblongata of the rat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1983 Jul;118(3):293–295. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1983.tb07273.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. J. Neural control of human airways in health and disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Dec;134(6):1289–1314. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.134.5.1289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlöf C., Dahlöf P., Lundberg J. M. Alpha 2-adrenoceptor-mediated inhibition of nerve stimulation-evoked release of neuropeptide Y (NPY)-like immunoreactivity in the pithed guinea-pig. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Nov 19;131(2-3):279–283. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90583-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel E. E., Kannan M., Davis C., Posey-Daniel V. Ultrastructural studies on the neuromuscular control of human tracheal and bronchial muscle. Respir Physiol. 1986 Jan;63(1):109–128. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(86)90034-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danser A. H., van den Ende R., Lorenz R. R., Flavahan N. A., Vanhoutte P. M. Prejunctional beta 1-adrenoceptors inhibit cholinergic transmission in canine bronchi. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Feb;62(2):785–790. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.62.2.785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doggrell S. A., Waldron J. B. The effects of 6-hydroxydopamine or (-)-noradrenaline treatment in vitro on noradrenergic transmission in the rat anococcygeus muscle. J Auton Pharmacol. 1982 Dec;2(4):231–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1982.tb00514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvinsson L., Ekblad E., Håkanson R., Wahlestedt C. Neuropeptide Y potentiates the effect of various vasoconstrictor agents on rabbit blood vessels. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Oct;83(2):519–525. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16516.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblad E., Edvinsson L., Wahlestedt C., Uddman R., Håkanson R., Sundler F. Neuropeptide Y co-exists and co-operates with noradrenaline in perivascular nerve fibers. Regul Pept. 1984 Apr;8(3):225–235. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(84)90064-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garzón J., Höllt V., Sánchez-Blázquez P. Neuropeptide Y is an inhibitor of neural function in the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig ileum. Peptides. 1986 Jul-Aug;7(4):623–629. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(86)90037-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunditz T., Håkanson R., Rerup C., Sundler F., Uddman R. Neuropeptide Y in the thyroid gland: neuronal localization and enhancement of stimulated thyroid hormone secretion. Endocrinology. 1984 Oct;115(4):1537–1542. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-4-1537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundström N., Andersson R. G., Wikberg J. E. Prejunctional alpha 2 adrenoceptors inhibit contraction of tracheal smooth muscle by inhibiting cholinergic neurotransmission. Life Sci. 1981 Jun 29;28(26):2981–2986. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90275-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Saria A., Franco-Cereceda A., Hökfelt T., Terenius L., Goldstein M. Differential effects of reserpine and 6-hydroxydopamine on neuropeptide Y (NPY) and noradrenaline in peripheral neurons. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1985 Jan;328(3):331–340. doi: 10.1007/BF00515563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Stjarne L. Neuropeptide Y (NPY) depresses the secretion of 3H-noradrenaline and the contractile response evoked by field stimulation, in rat vas deferens. Acta Physiol Scand. 1984 Mar;120(3):477–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1984.tb07410.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Terenius L., Hökfelt T., Martling C. R., Tatemoto K., Mutt V., Polak J., Bloom S., Goldstein M. Neuropeptide Y (NPY)-like immunoreactivity in peripheral noradrenergic neurons and effects of NPY on sympathetic function. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 Dec;116(4):477–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb07171.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martire M., Fuxe K., Pistritto G., Preziosi P., Agnati L. F. Neuropeptide Y enhances the inhibitory effects of clonidine on 3H-noradrenaline release in synaptosomes isolated from the medulla oblongata of the male rat. J Neural Transm. 1986;67(1-2):113–124. doi: 10.1007/BF01243364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews W. D., McCafferty G. P. Effects of chemical sympathectomy by 6-hydroxydopamine on alpha-adrenoceptor-mediated pressor responses in pithed rat. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1984 Mar-Apr;6(2):233–237. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198403000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadel J. A., Barnes P. J. Autonomic regulation of the airways. Annu Rev Med. 1984;35:451–467. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.35.020184.002315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernow J., Saria A., Lundberg J. M. Mechanisms underlying pre- and postjunctional effects of neuropeptide Y in sympathetic vascular control. Acta Physiol Scand. 1986 Feb;126(2):239–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1986.tb07811.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. B. Nerve supply to the lungs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 May;119(5):785–802. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.5.785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudehill A., Sollevi A., Franco-Cereceda A., Lundberg J. M. Neuropeptide Y (NPY) and the pig heart: release and coronary vasoconstrictor effects. Peptides. 1986 Sep-Oct;7(5):821–826. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(86)90101-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard M. N., Polak J. M., Allen J. M., Bloom S. R. Neuropeptide tyrosine (NPY): a newly discovered peptide is present in the mammalian respiratory tract. Thorax. 1984 May;39(5):326–330. doi: 10.1136/thx.39.5.326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stjärne L., Lundberg J. M., Astrand P. Neuropeptide Y--a cotransmitter with noradrenaline and adenosine 5'-triphosphate in the sympathetic nerves of the mouse vas deferens? A biochemical, physiological and electropharmacological study. Neuroscience. 1986 May;18(1):151–166. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90184-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundler F., Håkanson R., Ekblad E., Uddman R., Wahlestedt C. Neuropeptide Y in the peripheral adrenergic and enteric nervous systems. Int Rev Cytol. 1986;102:243–269. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61277-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. M., Paré P. D., Schellenberg R. R. Cholinergic and nonadrenergic mechanisms in human and guinea pig airways. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Apr;56(4):958–965. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.56.4.958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uddman R., Sundler F., Emson P. Occurrence and distribution of neuropeptide-Y-immunoreactive nerves in the respiratory tract and middle ear. Cell Tissue Res. 1984;237(2):321–327. doi: 10.1007/BF00217151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varndell I. M., Polak J. M., Allen J. M., Terenghi G., Bloom S. R. Neuropeptide tyrosine (NPY) immunoreactivity in norepinephrine-containing cells and nerves of the mammalian adrenal gland. Endocrinology. 1984 Apr;114(4):1460–1462. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-4-1460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlestedt C., Edvinsson L., Ekblad E., Håkanson R. Neuropeptide Y potentiates noradrenaline-evoked vasoconstriction: mode of action. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Sep;234(3):735–741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlestedt C., Yanaihara N., Håkanson R. Evidence for different pre-and post-junctional receptors for neuropeptide Y and related peptides. Regul Pept. 1986 Feb;13(3-4):307–318. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(86)90048-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


