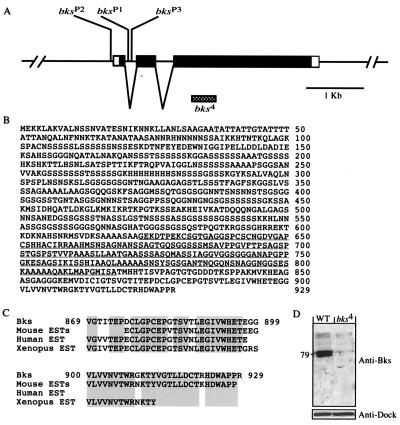
Figure 2.
Molecular characterization of the brakeless gene. (A) Genomic structure of the brakeless gene. P element insertion sites for bksP1 and bksP3 are located within the first intron, 14 bp and ≈140 bp (based on the Berkeley Drosophila Genome Project database of transposon insertions) downstream of the exon/intron boundary, respectively. The P element insertion site for bksP2 is located 11 bp upstream of the first exon. The sequence deleted in bks4 is indicated as the shaded box. Filled boxes indicate the putative translated sequences whereas open boxes indicate untranslated sequences. (B) The predicted protein sequence of Brakeless. The sequence (amino acids 623–818) used to raise antiserum in rabbit is underlined. (C) Alignment of the Brakeless protein and homologous vertebrate sequences (ESTs). Identical amino acids are stippled. (D) Western blot analysis of extracts made from five third-instar larval eye-brain complexes. Anti-Bks antibody detected a single band at ≈80 kDa in the wild type, but not in bks4 homozygous mutants.