Abstract
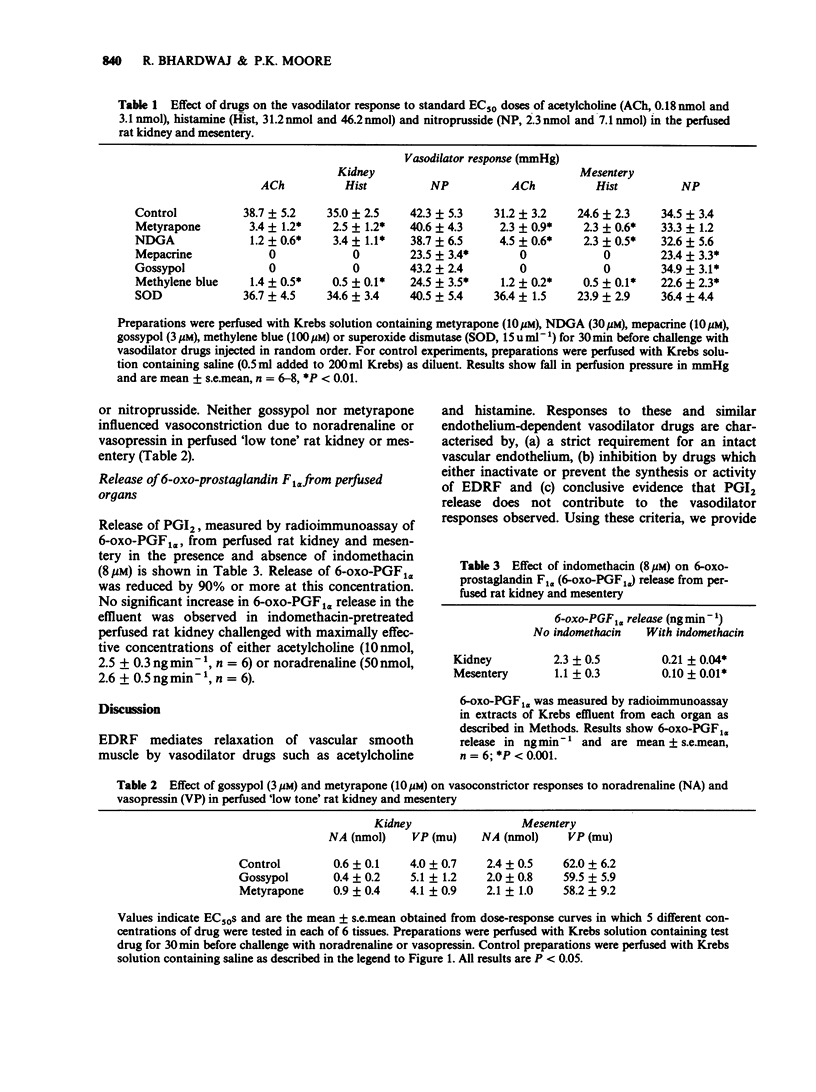
1. The role of endothelium-derived relaxing factor (EDRF) in the action of vasodilator (acetylcholine, histamine, nitroprusside) and vasoconstrictor (noradrenaline, vasopressin) drugs on vascular resistance in the isolated perfused kidney and mesentery of the rat was studied. 2. Acetylcholine (EC50 = 0.18 +/- 0.05 nmol and 3.1 +/- 0.06 nmol, n = 8) and histamine (EC50 = 31.2 +/- 4.9 nmol and 46.2 +/- 3.9 nmol, n = 8) produced dose-related vasodilatation in noradrenaline-preconstricted (i.e. 'high tone') rat renal and mesenteric blood vessels. The response to both vasodilators (but not nitroprusside) was abolished by infusion of CHAPS (4.7 mg ml-1, 30 s). By use of an immunocytochemical staining procedure CHAPS was demonstrated to remove vascular endothelial cells lining intrarenal blood vessels. 3. Gossypol (3 microM), metyrapone (10 microM) and nordihydroguaiaretic acid, (NDGA, 30 microM), presumed inhibitors of EDRF biosynthesis, reduced or abolished the response to acetylcholine and histamine in perfused kidney and mesentery of the rat without affecting vasodilatation due to nitroprusside. Mepacrine (10 microM) similarly abolished the response to acetylcholine and histamine but in addition, reduced the response to nitroprusside in both preparations. 4. Methylene blue (100 microM), a presumed antagonist of the effect of EDRF, abolished vasodilatation due to acetylcholine and histamine and reduced the response to nitroprusside in perfused rat kidney and mesentery. Superoxide dismutase, SOD (15 u ml-1), was without effect.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




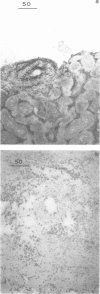
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alheid U., Dudel C., Förstermann U. Selective inhibition by gossypol of endothelium-dependent relaxations augments relaxations to glyceryl trinitrate in rabbit coeliac artery. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Sep;92(1):237–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11317.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. M., Blackwell G. J., Flower R. J., McGiff J. C., Mullane K. M., Vane J. R. Genetic hypertension in rats is accompanied by a defect in renal prostaglandin catabolism. Nature. 1976 Apr 15;260(5552):582–586. doi: 10.1038/260582a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arvieux J., Willis A. C., Williams A. F. MRC OX-45 antigen: a leucocyte/endothelium rat membrane glycoprotein of 45,000 molecular weight. Mol Immunol. 1986 Sep;23(9):983–990. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90129-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azuma H., Ishikawa M., Sekizaki S. Endothelium-dependent inhibition of platelet aggregation. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Jun;88(2):411–415. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10218.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry C. N., Griffiths R. J., Hoult J. R., Moore P. K., Taylor G. W. Identification of 6-oxo-prostaglandin E1 as a naturally occurring prostanoid generated by rat lung. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Feb;87(2):327–335. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10821.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry P. D., Gillis C. N. Evidence for the role of endothelium-derived relaxing factor in acetylcholine-induced vasodilatation in the intact lung. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 May;241(2):516–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba S., Tsukada M. Potentiation of KCl-induced vasoconstriction by saponin treatment in isolated canine mesenteric arteries. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1984 Dec;36(4):535–537. doi: 10.1254/jjp.36.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F., Carvalho M. H., Khan M. T., Matsunaga K. Evidence for endothelium-dependent vasodilation of resistance vessels by acetylcholine. Blood Vessels. 1987;24(3):145–149. doi: 10.1159/000158689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F. Role of endothelium in responses of vascular smooth muscle. Circ Res. 1983 Nov;53(5):557–573. doi: 10.1161/01.res.53.5.557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F., Zawadzki J. V. The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):373–376. doi: 10.1038/288373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlong B., Henderson A. H., Lewis M. J., Smith J. A. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor inhibits in vitro platelet aggregation. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Apr;90(4):687–692. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11221.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Förstermann U., Goppelt-Strübe M., Frölich J. C., Busse R. Inhibitors of acyl-coenzyme A:lysolecithin acyltransferase activate the production of endothelium-derived vascular relaxing factor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Jul;238(1):352–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith T. M., Edwards D. H., Lewis M. J., Newby A. C., Henderson A. H. The nature of endothelium-derived vascular relaxant factor. Nature. 1984 Apr 12;308(5960):645–647. doi: 10.1038/308645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryglewski R. J., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Superoxide anion is involved in the breakdown of endothelium-derived vascular relaxing factor. Nature. 1986 Apr 3;320(6061):454–456. doi: 10.1038/320454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzmann S. Endothelium-induced relaxation by acetylcholine associated with larger rises in cyclic GMP in coronary arterial strips. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1982;8(6):409–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Burke T. M., Wood K. S., Wolin M. S., Kadowitz P. J. Association between cyclic GMP accumulation and acetylcholine-elicited relaxation of bovine intrapulmonary artery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Mar;228(3):682–690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb F. S., King C. M., Harrell K., Burkel W., Webb R. C. Free radical-mediated endothelial damage in blood vessels after electrical stimulation. Am J Physiol. 1987 May;252(5 Pt 2):H1041–H1046. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1987.252.5.H1041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCGREGOR D. D. THE EFFECT OF SYMPATHETIC NERVE STIMULATION OF VASOCONSTRICTOR RESPONSES IN PERFUSED MESENTERIC BLOOD VESSELS OF THE RAT. J Physiol. 1965 Mar;177:21–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W., Villani G. M., Jothianandan D., Furchgott R. F. Selective blockade of endothelium-dependent and glyceryl trinitrate-induced relaxation by hemoglobin and by methylene blue in the rabbit aorta. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Mar;232(3):708–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. Y., Sammons R. Alkaline phosphatase and peroxidase for double immunoenzymatic labelling of cellular constituents. J Clin Pathol. 1978 May;31(5):454–460. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.5.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ferrige A. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):524–526. doi: 10.1038/327524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport R. M., Murad F. Agonist-induced endothelium-dependent relaxation in rat thoracic aorta may be mediated through cGMP. Circ Res. 1983 Mar;52(3):352–357. doi: 10.1161/01.res.52.3.352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silin P. J., Strulowitz J. A., Wolin M. S., Belloni F. L. Absence of a role for superoxide anion, hydrogen peroxide and hydroxyl radical in endothelium-mediated relaxation of rabbit aorta. Blood Vessels. 1985;22(2):65–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart D. J., Münzel T., Bassenge E. Reversal of acetylcholine-induced coronary resistance vessel dilation by hemoglobin. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Apr 14;136(2):239–242. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90717-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanhoutte P. M., Rubanyi G. M., Miller V. M., Houston D. S. Modulation of vascular smooth muscle contraction by the endothelium. Annu Rev Physiol. 1986;48:307–320. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.48.030186.001515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]