Abstract
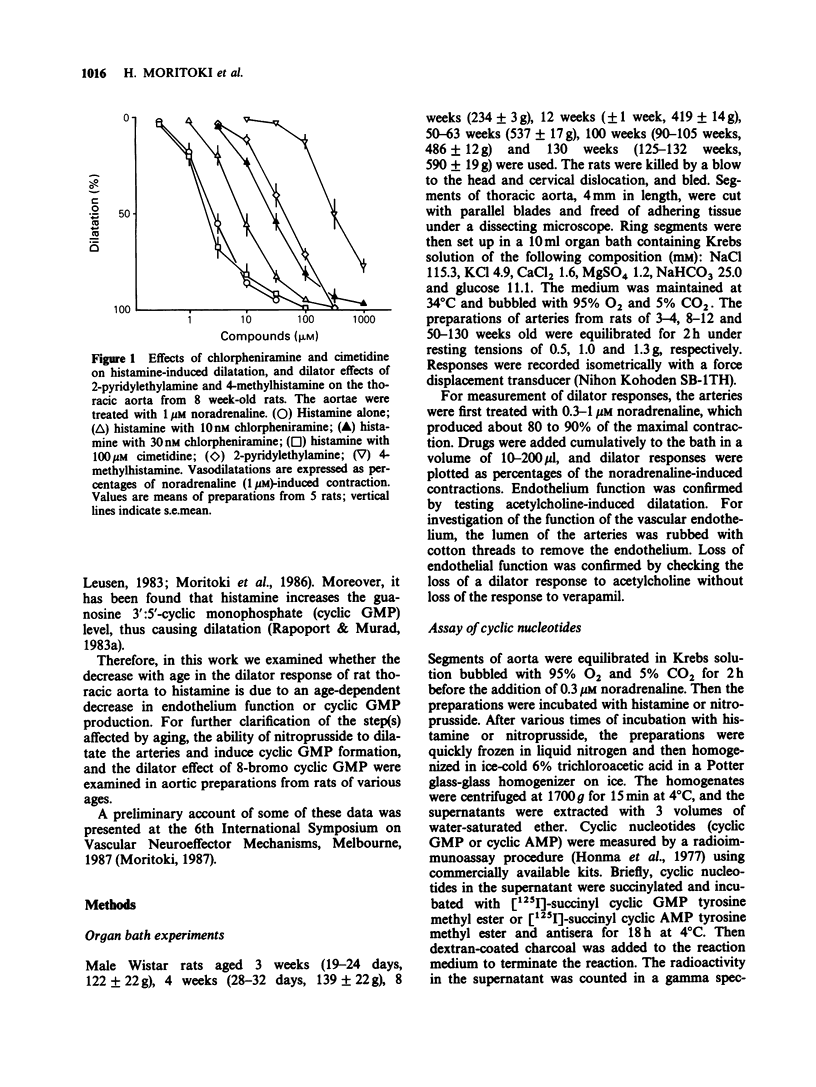
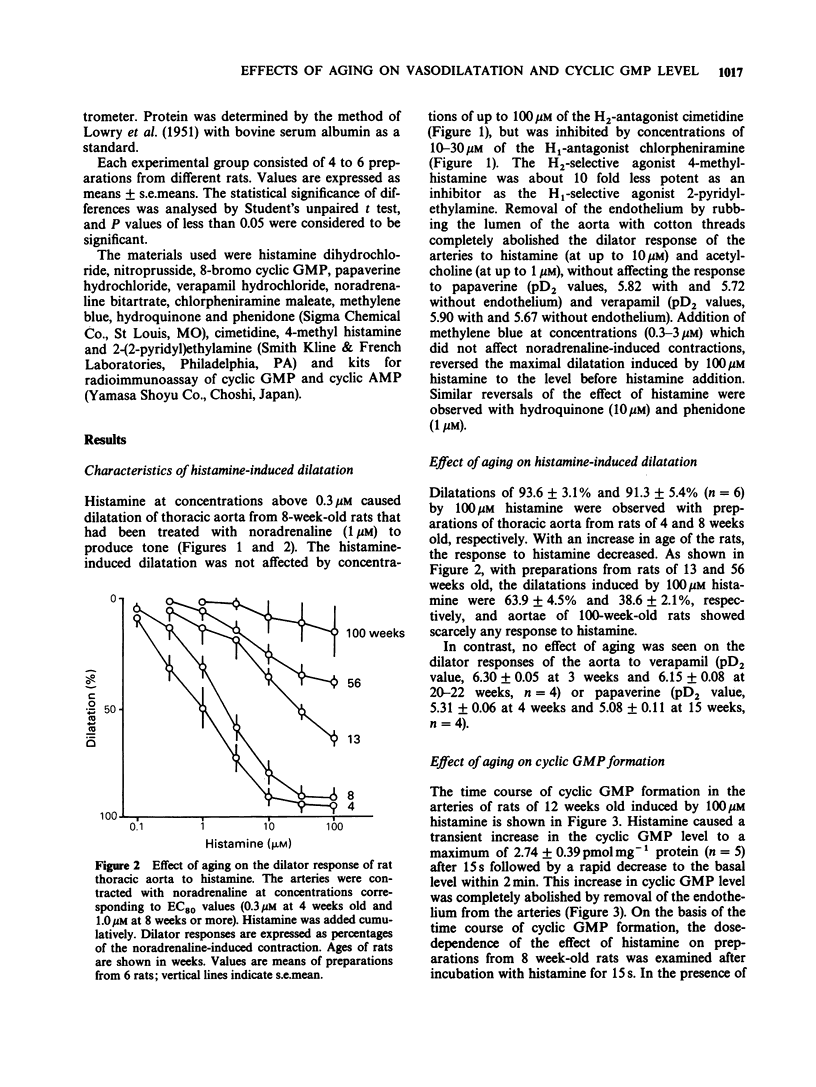
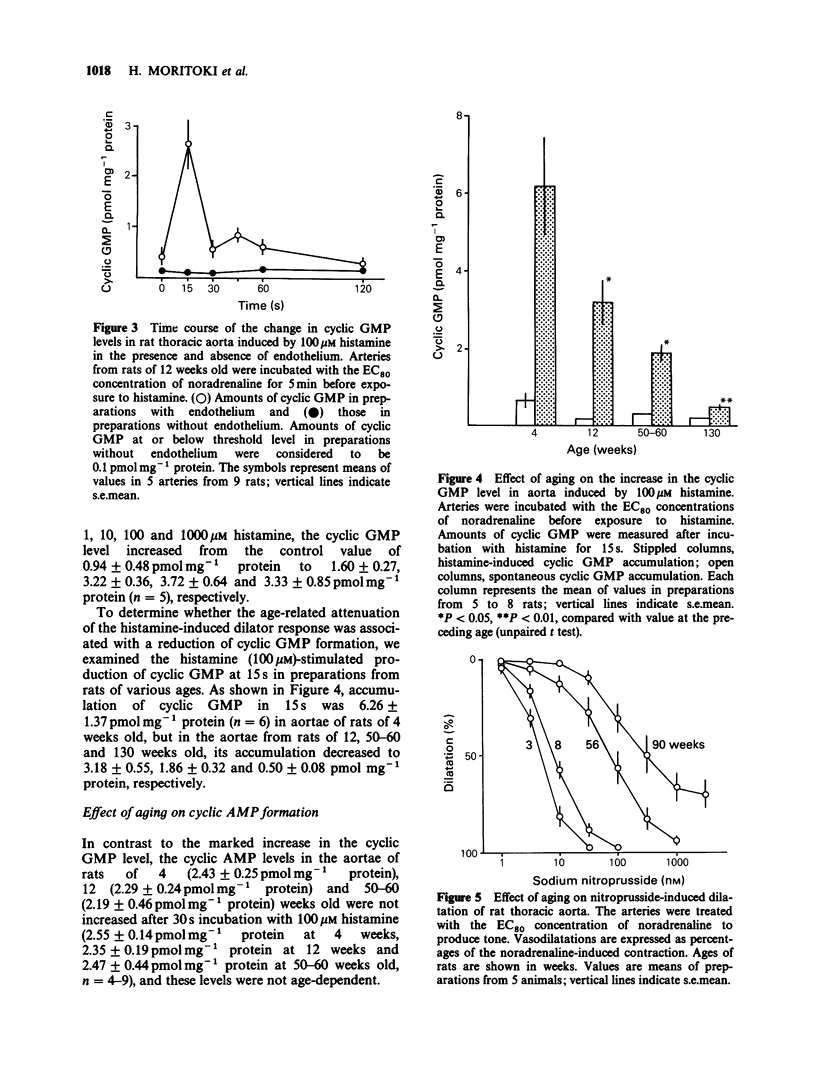
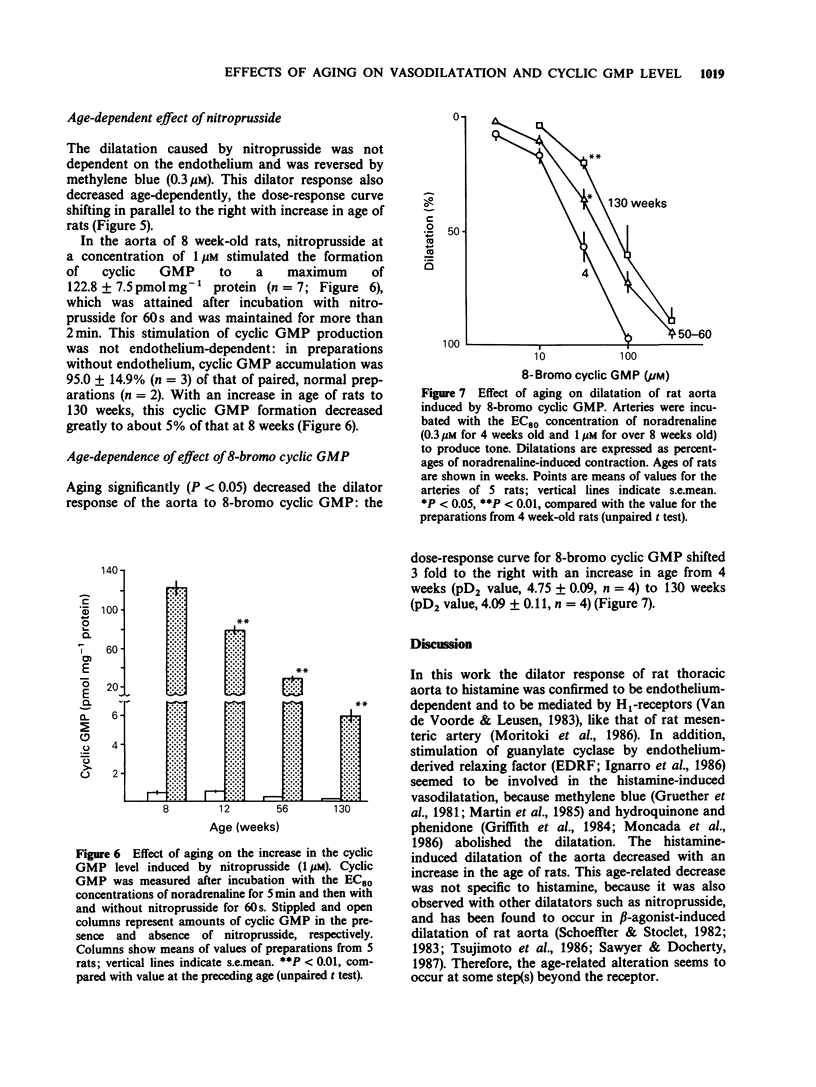
1. The effects of aging on histamine-induced vasodilatation and cyclic GMP production in rat thoracic aorta were investigated. 2. This histamine-induced dilatation of the aorta was mediated by H1-receptors and was dependent on the endothelium. 3. Histamine induced the greatest dilatation of arteries of 3-4 week old rats, progressively less of those of rats of 8 to 56 weeks old, and scarcely detectable dilatation of those of 100 week old rats. 4. Histamine induced cyclic GMP production in aorta from rats of 4 weeks old, with no change in the cyclic AMP level. This increase in the cyclic GMP level induced by histamine also decreased with age, being about 70% as great at 8 weeks, 50% as great at 50-60 weeks, and 10% as great at 130 weeks of age. 5. Removal of the endothelium completely abolished the histamine-induced increase in cyclic GMP. 6. The dilator effect of nitroprusside, which enhances cyclic GMP production by stimulating guanylate cyclase directly (not indirectly via the endothelium derived relaxing factor, EDRF), also showed age-related attenuation. 7. The dilator effect of 8-bromo cyclic GMP, which stimulates cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase, also decreased during aging. 8. These results suggest that aging reduces the ability of the endothelium to produce EDRF, which stimulates guanylate cyclase, and so decreases cyclic GMP production. Thus the decreased dilator response of the arteries to histamine during aging is probably due to both loss of endothelial function and reduction of guanylate cyclase activity. Alteration of cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase activity may also participate in the age-related changes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhalla R. C., Sharma R. V., Ramanathan S. Ontogenetic development of isoproterenol subsensitivity of myocardial adenylate cyclase and beta-adrenergic receptors in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 3;632(4):497–506. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90326-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F. Role of endothelium in responses of vascular smooth muscle. Circ Res. 1983 Nov;53(5):557–573. doi: 10.1161/01.res.53.5.557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Förstermann U., Mülsch A., Böhme E., Busse R. Stimulation of soluble guanylate cyclase by an acetylcholine-induced endothelium-derived factor from rabbit and canine arteries. Circ Res. 1986 Apr;58(4):531–538. doi: 10.1161/01.res.58.4.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith T. M., Edwards D. H., Lewis M. J., Henderson A. H. Evidence that cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) mediates endothelium-dependent relaxation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Jun 7;112(2):195–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90496-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith T. M., Edwards D. H., Lewis M. J., Newby A. C., Henderson A. H. The nature of endothelium-derived vascular relaxant factor. Nature. 1984 Apr 12;308(5960):645–647. doi: 10.1038/308645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruetter C. A., Kadowitz P. J., Ignarro L. J. Methylene blue inhibits coronary arterial relaxation and guanylate cyclase activation by nitroglycerin, sodium nitrite, and amyl nitrite. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1981 Feb;59(2):150–156. doi: 10.1139/y81-025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honma M., Satoh T., Takezawa J., Ui M. An ultrasensitive method for the simultaneous determination of cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP in small-volume samples from blood and tissue. Biochem Med. 1977 Dec;18(3):257–273. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(77)90060-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyland L., Warnock P., Docherty J. R. Age-related alterations in alpha 1- and beta-adrenoceptors mediated responsiveness of rat aorta. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Jan;335(1):50–53. doi: 10.1007/BF00165035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Harbison R. G., Wood K. S., Kadowitz P. J. Activation of purified soluble guanylate cyclase by endothelium-derived relaxing factor from intrapulmonary artery and vein: stimulation by acetylcholine, bradykinin and arachidonic acid. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Jun;237(3):893–900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Kadowitz P. J. The pharmacological and physiological role of cyclic GMP in vascular smooth muscle relaxation. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1985;25:171–191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.25.040185.001131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugnier C., Stoclet J. C. Age related changes in cardiac and aortic phosphodiesterase activities in normotensive and hypertensive rats. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Dec 15;28(24):3581–3587. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90403-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W., Villani G. M., Jothianandan D., Furchgott R. F. Selective blockade of endothelium-dependent and glyceryl trinitrate-induced relaxation by hemoglobin and by methylene blue in the rabbit aorta. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Mar;232(3):708–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Gryglewski R. J. Mechanism of action of some inhibitors of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9164–9168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moritoki H., Hosoki E., Ishida Y. Age-related decrease in endothelium-dependent dilator response to histamine in rat mesenteric artery. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Jul 15;126(1-2):61–67. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90738-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell S. R., Wanstall J. C. Beta-1 and beta-2 adrenoceptor-mediated responses in preparations of pulmonary artery and aorta from young and aged rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Mar;228(3):733–738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popescu L. M., Panoiu C., Hinescu M., Nutu O. The mechanism of cGMP-induced relaxation in vascular smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Jan 8;107(3):393–394. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90269-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport R. M., Draznin M. B., Murad F. Endothelium-dependent relaxation in rat aorta may be mediated through cyclic GMP-dependent protein phosphorylation. Nature. 1983 Nov 10;306(5939):174–176. doi: 10.1038/306174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport R. M., Draznin M. B., Murad F. Sodium nitroprusside-induced protein phosphorylation in intact rat aorta is mimicked by 8-bromo cyclic GMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6470–6474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport R. M., Murad F. Agonist-induced endothelium-dependent relaxation in rat thoracic aorta may be mediated through cGMP. Circ Res. 1983 Mar;52(3):352–357. doi: 10.1161/01.res.52.3.352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport R. M., Murad F. Endothelium-dependent and nitrovasodilator-induced relaxation of vascular smooth muscle: role of cyclic GMP. J Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphor Res. 1983;9(4-5):281–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer R., Docherty J. R. Reduction with age in the relaxation to beta-adrenoceptor agonists and other vasodilators in rat aorta. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Jul;336(1):60–63. doi: 10.1007/BF00177751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoeffter P., Stoclet J. C. Age-related decrease of in vitro isoproterenol-induced cyclic AMP accumulation in rat aorta. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Jan 22;77(2-3):183–186. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoeffter P., Stoclet J. C. Ageing as a factor governing the effect of isoproterenol on the cyclic AMP level in isolated aorta from spontaneously hypertensive and normotensive rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Jan 21;86(3-4):481–484. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90201-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto G., Lee C. H., Hoffman B. B. Age-related decrease in beta adrenergic receptor-mediated vascular smooth muscle relaxation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Nov;239(2):411–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Voorde J., Leusen I. Role of the endothelium in the vasodilator response of rat thoracic aorta to histamine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Jan 28;87(1):113–120. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90056-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


