Abstract
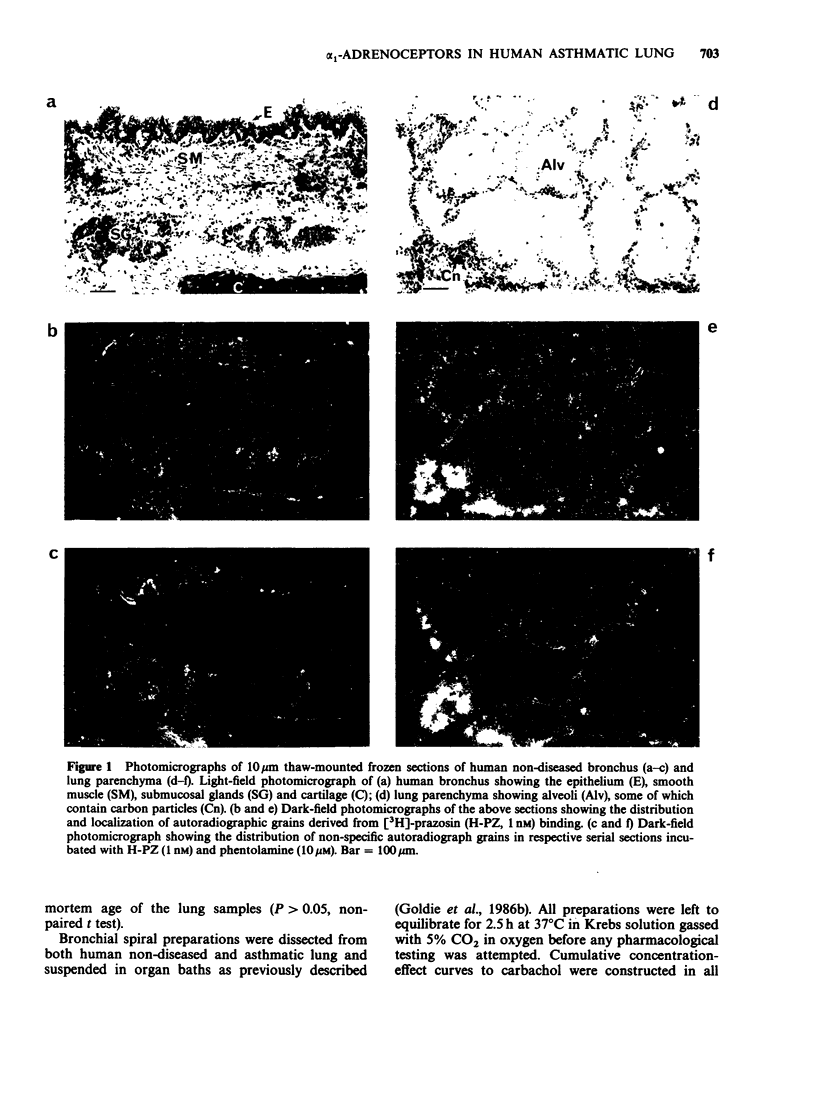
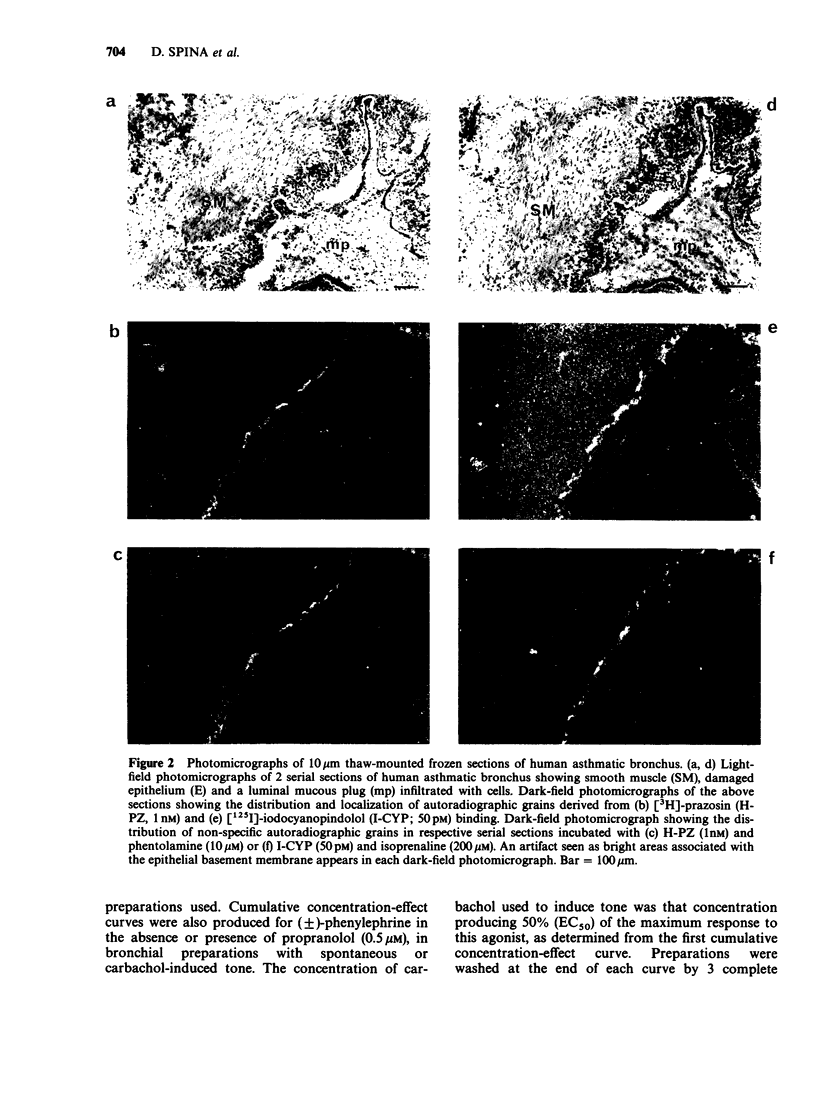
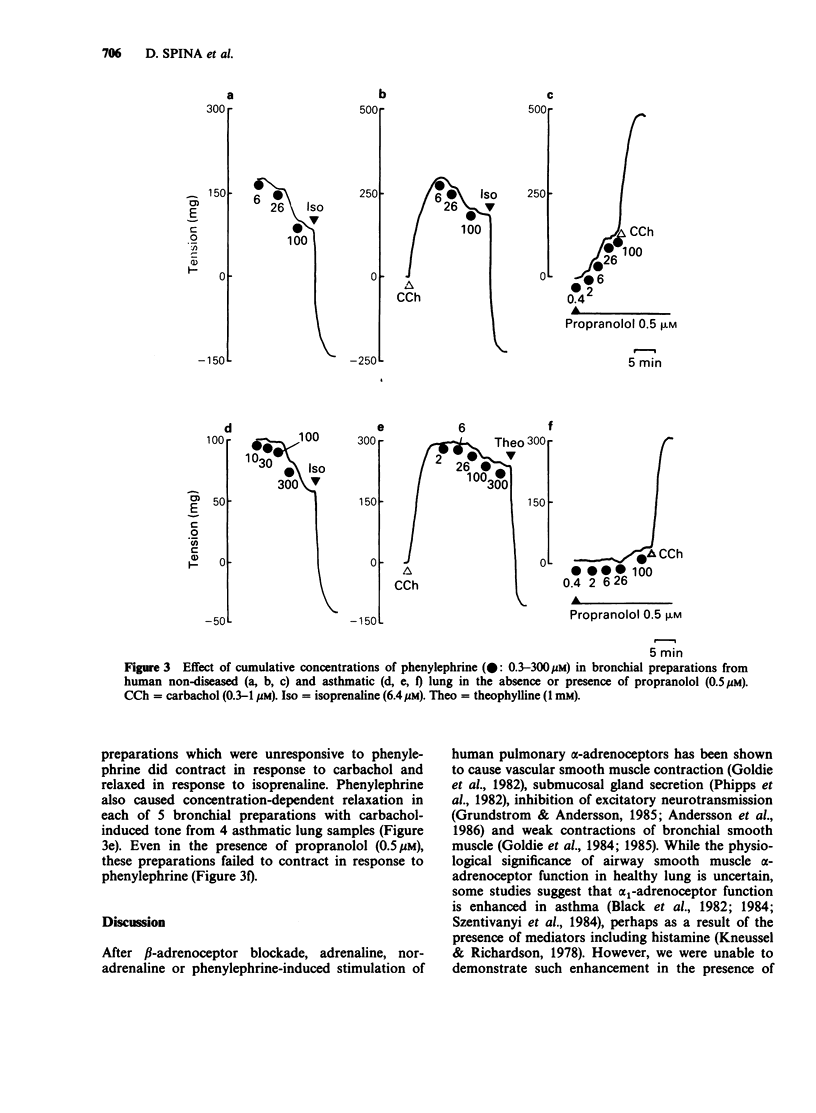
1. The autoradiographic distribution of alpha 1-adrenoceptors was investigated in non-diseased and asthmatic human lung by use of [3H]-prazosin (H-PZ). To validate binding and autoradiographic methods, H-PZ binding was also measured in rat heart. 2. Significant levels of specific H-PZ binding were detected in sections of rat heart. This binding was associated with a single class of non-interacting sites of high affinity (dissociation constant, Kd = 1.17 +/- 0.26 nM). The maximum binding capacity (Bmax) was 59.5 +/- 4.5 fmol mg-1 protein. 3. In sharp contrast, very low levels of specific H-PZ binding were found in both human nondiseased and asthmatic bronchus, although a high level of binding of [125I]-iodocyanopindolol (I-CYP, 50 pM) to beta-adrenoceptors was detected in these airways. Furthermore, very low levels of autoradiographic grains representing specific H-PZ binding were found in all airway structures in human non-diseased or asthmatic lung parenchyma. 4. Consistent with these data, the alpha-adrenoceptor agonist phenylephrine failed to induce significant increases in tone in bronchi isolated from either non-diseased or asthmatic human lung. Results indicate that asthma does not involve significant increases in airway alpha 1-adrenoceptor function.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes P. J., Basbaum C. B., Nadel J. A., Roberts J. M. Pulmonary alpha-adrenoceptors: autoradiographic localization using [3H]prazosin. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Mar 18;88(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90391-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. J., Dollery C. T., MacDermot J. Increased pulmonary alpha-adrenergic and reduced beta-adrenergic receptors in experimental asthma. Nature. 1980 Jun 19;285(5766):569–571. doi: 10.1038/285569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. J., Karliner J. S., Dollery C. T. Human lung adrenoreceptors studied by radioligand binding. Clin Sci (Lond) 1980 Jun;58(6):457–461. doi: 10.1042/cs0580457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. J. Neural control of human airways in health and disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Dec;134(6):1289–1314. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.134.5.1289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. J., Skoogh B. E., Nadel J. A., Roberts J. M. Postsynaptic alpha 2-adrenoceptors predominate over alpha 1-adrenoceptors in canine tracheal smooth muscle and mediate neuronal and hormonal alpha-adrenergic contraction. Mol Pharmacol. 1983 May;23(3):570–575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P., Karliner J., Hamilton C., Dollery C. Demonstration of alpha 1-adrenoceptors in guinea pig lung using 3H-prazosin. Life Sci. 1979 Oct 1;25(14):1207–1214. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90462-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudouin S. V., Aitman T. J., Johnson A. J. Prazosin in the treatment of chronic asthma. Thorax. 1988 May;43(5):385–387. doi: 10.1136/thx.43.5.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. L., Salome C. M., Yan K., Shaw J. Comparison between airways response to an alpha-adrenoceptor agonist and histamine in asthmatic and non-asthmatic subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1982 Sep;14(3):464–466. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1982.tb02012.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. L., Salome C., Yan K., Shaw J. The action of prazosin and propylene glycol on methoxamine-induced bronchoconstriction in asthmatic subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1984 Sep;18(3):349–353. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1984.tb02475.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldie R. G., Papadimitriou J. M., Paterson J. W., Rigby P. J., Spina D. Autoradiographic localization of beta-adrenoceptors in pig lung using [125I]-iodocyanopindolol. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Jul;88(3):621–628. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10243.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldie R. G., Paterson J. W., Spina D., Wale J. L. Classification of beta-adrenoceptors in human isolated bronchus. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Apr;81(4):611–615. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16125.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldie R. G., Paterson J. W., Wale J. L. Pharmacological responses of human and porcine lung parenchyma, bronchus and pulmonary artery. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Aug;76(4):515–521. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09248.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldie R. G., Spina D., Henry P. J., Lulich K. M., Paterson J. W. In vitro responsiveness of human asthmatic bronchus to carbachol, histamine, beta-adrenoceptor agonists and theophylline. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1986 Dec;22(6):669–676. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1986.tb02956.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. P., Kamburoff P. L., Prime F. J., Arbab A. G. Thymoxamine and airways obstruction. Lancet. 1972 Jun 10;1(7763):1288–1288. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundström N., Andersson R. G. Inhibition of the cholinergic neurotransmission in human airways via prejunctional alpha-2-adrenoceptors. Acta Physiol Scand. 1985 Nov;125(3):513–517. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1985.tb07749.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guicheney P., Meyer P. Binding of [3H]-prazosin and [3H]-dihydroergocryptine to rat cardiac alpha-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 May;73(1):33–39. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb16768.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ind P. W., Dollery C. T. Pulmonary adrenoceptors and asthma. Agents Actions Suppl. 1983;13:213–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kneussl M. P., Richardson J. B. Alpha-adrenergic receptors in human and canine tracheal and bronchial smooth muscle. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1978 Aug;45(2):307–311. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1978.45.2.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren B. R., Ekström T., Andersson R. G. The effect of inhaled clonidine in patients with asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Aug;134(2):266–269. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.134.2.266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathé A. A., Aström A., Persson N. A. Some bronchoconstricting and bronchodilating responses of human isolated bronchi: evidence for the existence of -adrenoceptors. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1971 Dec;23(12):905–910. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1971.tb09891.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muntz K. H., Garcia C., Hagler H. K. alpha 1-Receptor localization in rat heart and kidney using autoradiography. Am J Physiol. 1985 Sep;249(3 Pt 2):H512–H519. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1985.249.3.H512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel K. R., Kerr J. W. Effect of alpha receptor blocking drug, thymoxamine, on allergen induced bronchoconstriction in extrinsic asthma. Clin Allergy. 1975 Sep;5(3):311–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1975.tb01868.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel K. R., Kerr J. W. The airways response to phenylephrine after blockade of alpha and beta receptors in extrinsic bronchial asthma. Clin Allergy. 1973 Dec;3(4):439–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1973.tb01351.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peatfield A. C., Richardson P. S. The control of mucin secretion into the lumen of the cat trachea by alpha- and beta-adrenoceptors, and their relative involvement during sympathetic nerve stimulation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Jul 30;81(4):617–626. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90351-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phipps R. J., Williams I. P., Richardson P. S., Pell J., Pack R. J., Wright N. Sympathomimetic drugs stimulate the output of secretory glycoproteins from human bronchi in vitro. Clin Sci (Lond) 1982 Jul;63(1):23–28. doi: 10.1042/cs0630023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snashall P. D., Boother F. A., Sterling G. M. The effect of alpha-adrenoreceptor stimulation on the airways of normal and asthmatic man. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1978 Mar;54(3):283–289. doi: 10.1042/cs0540283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svedmyr N. Szentivanyi's hypothesis of asthma. Eur J Respir Dis Suppl. 1984;136:59–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szentivanyi A., Heim O., Schultze P. Changes in adrenoceptor densities in membranes of lung tissue and lymphocytes from patients with atopic disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1979;332:295–298. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1979.tb47123.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szentivanyi A. The radioligand binding approach in the study of lymphocytic adrenoceptors and the constitutional basis of atopy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1980 Jan;65(1):5–11. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(80)90170-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson N. C., Daniel E. E., Hargreave F. E. Role of smooth muscle alpha 1-receptors in nonspecific bronchial responsiveness in asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Sep;126(3):521–525. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.3.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utting J. A. Alpha-adrenergic blockade in severe asthma. Br J Dis Chest. 1979 Jul;73(3):317–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xue Q. F., Maurer R., Engel G. Selective distribution of beta- and alpha 1-adrenoceptors in rat lung visualized by autoradiography. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1983 Dec;266(2):308–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]