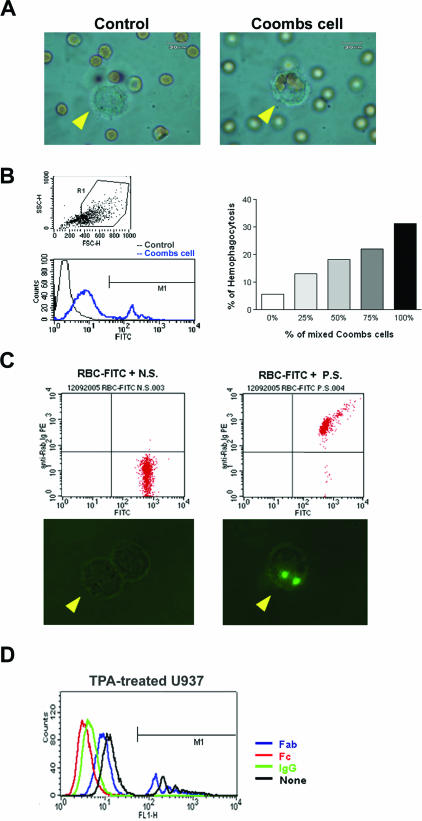
Figure 5.
Anti-red cell/heterophile antibody-mediated phagocytosis assay in vitro and ex vivo. A: In vitro study to show the specific engulfment of Coombs cells, but not the control RBCs, by activated macrophages (arrowhead). B: In vitro study to show the dose-dependent manner of phagocytosis of Coombs cells by activated macrophages. TPA-activated U937 cells were gated (top left). The FITC intensities were gated at M1 region (bottom left). The activities of RBC phagocytosis by macrophages increased with the ratio of Coombs cells (right). C: Ex vivo assay of phagocytosis of antibody-coated rabbit red cells by TPA-activated rabbit monocytes. Top panel shows flow cytometric analysis of FITC-labeled RBCs treated with either control serum (N.S.) or HVP-infected serum (P.S.) (top). The activated macrophages engulfed only the red cells incubated with HVP-infected serum (bottom right), but not with control serum (bottom left). D: IgG molecules and Fc fragments, but not Fab fragments, completely inhibited antibody-mediated phagocytosis of Coombs cells by TPA-treated U937 cells. The FITC intensities over the M1-defined region mark the measured fluorescence intensity fraction of Coombs cell phagocytosis.