Figure 3.
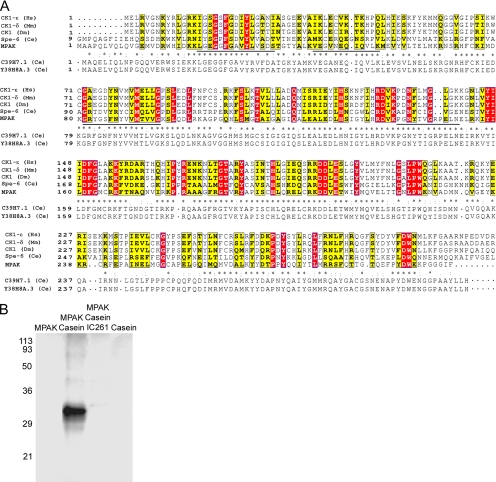
Amino acid sequence homology and enzymatic activity indicate that the 34-kDa protein is a member of the casein kinase 1 family of Ser/Thr kinases. (A) Alignment of the predicted sequence of the 34-kDa protein (now designated MPAK) with four representative sequences from the casein kinase 1 family: CK1-ε from humans (Hs, NP_001885), CK1-δ from mouse (Mm, NP_620690), CK1 from Drosophila melanogaster (Dm, AAC39134), and spe-6 from C. elegans (Ce, NP_499482). Completely conserved residues are highlighted in red and nearly conserved ones in yellow. The sequence of MPAK (AY326289) is also aligned with that of its C. elegans homolog, C39H7.1; asterisks represent identical residues, colons indicate highly conservative substitutions, and periods denote less conservative differences. The sequence of Y38H8A.3, a closely related predicted protein from C. elegans, is shown below that of C39H7.1. The four peptide sequences obtained via proteolysis of MPAK and used to generate oligonucleotides for RT-PCR are underlined in the MPAK sequence. The sequence of each peptide is identical to the predicted amino acid sequence from the MPAK cDNA. (B) Autoradiogram of an SDS-PAGE gel of kinase assays of purified MPAK. Components incubated with 32P-ATP in the kinase assays are indicated above the gel lanes. Casein was phosphorylated by MPAK and the casein 1 kinase inhibitor, IC 261, blocked this activity. No phosphorylation was detected with MPAK or casein alone. Numerals indicate the positions of molecular weight markers in kDa.