Figure 5.
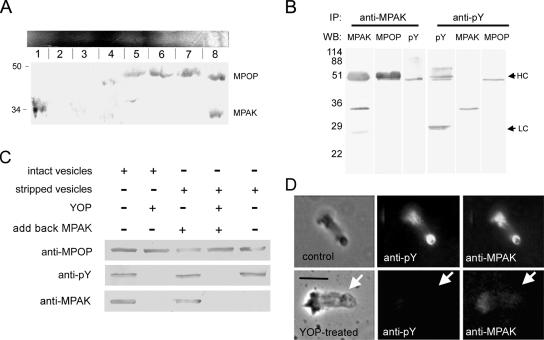
MPAK binds to phosphorylated MPOP. (A) Two-dimensional native/SDS-PAGE gel electrophoresis of S100. A Coomassie-stained native gel is shown horizontally at the top. An identical gel was cut into eight slices as indicated, and each slice was loaded into a well of a 15% SDS-PAGE gel, blotted, and probed with both anti-MPOP and anti-MPAK. Slice 8 from the native gel contained both proteins. Slice 1 contained MPAK but no MPOP; slices 5–7 contained MPOP but no MPAK. (B) Western blots of the proteins obtained by immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-MPAK and anti-pY antibodies. WB denotes the antibody used for Western blots of the gel lanes indicated. In addition to its target antigen, anti-MPAK also pulled down tyrosine phosphorylated MPOP, detectable by both anti-MPOP and anti-pY on Western blots. HC and LC indicate the positions of rabbit and mouse Ig heavy and light chains, respectively. Note that because anti-MPAK and anti-MPOP were produced in rabbits the secondary anti-rabbit IgG used for detection labeled the immunoglobulin used for immunoprecipitation. Ig heavy chain migrates slightly slower than the 48-kDa MPOP, the position of which can be seen in the lane probed with anti-pY, a mouse monoclonal that does not react with rabbit IgG. Anti-pY coimmunoprecipitated MPAK and MPOP detected on Western blots probed with anti-MPAK and anti-MPOP antibodies. Numerals indicate positions of molecular-weight markers (in kDa). (C) Vesicle pulldown assay. Selected portions of Western blots of material pelleted after incubation of vesicles (intact or stripped with 1.5M KCl) with or without MPAK. Incubation conditions are shown above the Western blot panels. In preparations treated with YOP (second and fourth lanes), the vesicles were incubated with the tyrosine phosphatase, washed in assay buffer, and then pelleted. Antibodies used for Western blots are shown at the left. (D) Effect of YOP on the presence of MPAK in fibers. The top series of panels shows a control fiber, washed with KPM assembly buffer, fixed, and labeled with anti-pY and anti-MPAK antibodies by indirect immunofluorescence. The bottom panels show a fiber treated with buffer containing YOP before fixation and labeling. YOP treatment abolished labeling of both phosphorylated MPOP and MPAK at the vesicle-bearing end of the fiber. Arrows indicate the position of the vesicle on each fiber. Bar, 5 μm.