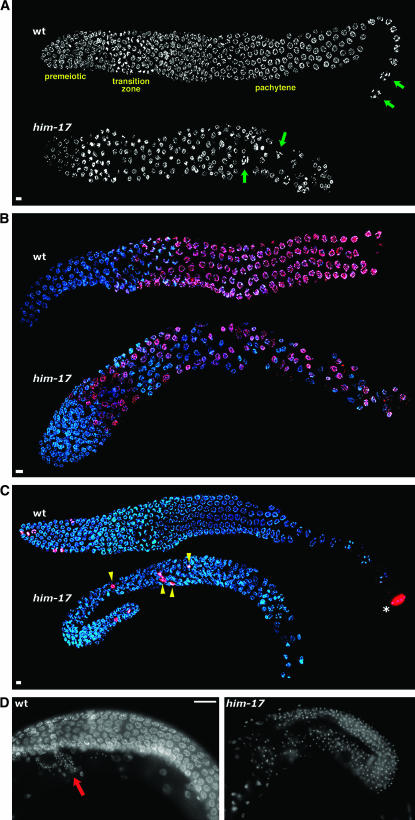
Figure 1.—
him-17 25° hermaphrodites exhibit defects in germline organization. (A) DAPI-stained germlines of wild-type and him-17(me24) hermaphrodites raised at 25°. In the wild-type germline, nuclei at diakinesis, the last stage of meiotic prophase, are seen only in the most proximal region of the gonad (green arrows). These nuclei are characterized by highly compact chromosomes that are well separated from each other. In the him-17 germline, diakinesis-like nuclei (green arrows) are seen in more distal regions interspersed with pachytene-like nuclei, indicating perturbed spatial organization of meiotic prophase substages. (B) Hermaphrodite germlines stained with HIM-3 antibody (red) and DAPI (blue). In the wild-type germline, HIM-3 antibody does not stain premeiotic nuclei but stains all meiotic prophase nuclei beginning in the transition zone. In the him-17(ok424) 25° germline, HIM-3-negative nuclei are seen throughout the gonad, interspersed with meiotic prophase nuclei. (C) Hermaphrodite germlines stained with H3S10p antibody (red) and DAPI (blue). In the wild-type germline, anti-H3S10p-stained mitotic figures are seen only in the distal tip of the gonad (left). The asterisk indicates a nucleus at the end of the diakinesis stage, which is also brightly stained with anti-H3S10; mitotic figures are easily distinguished from late diakinesis nuclei on the basis of the appearance of DAPI-stained chromatin. In the him-17(me24) 25° germline, mitotic figures are observed in ectopic positions (yellow arrowheads). (D) Images of whole-mount adult hermaphrodite worms stained with DAPI. The wild-type germline is undergoing oogenesis (oocyte nuclei are in a different focal plane); the small DAPI-stained foci in the region indicated by the red arrow correspond to the nuclei of sperm stored in the spermatheca. The him-17(me24) 25° gonad is filled with small DAPI foci corresponding to sperm nuclei, indicating a failure to switch from spermatogenesis to oogenesis. In A–D, worms were shifted to 25° at the L3 stage; upon reaching late L4, worms were selected for subsequent cytological analysis and maintained at 25° for 20–24 hr prior to fixation. For A–C, gonad dissection, fixation, staining, and imaging using the Deltavision deconvolution microscopy system were conducted as described (Reddy and Villeneuve 2004). Bars in A–C, 4 μm. Images are projections through 3D data stacks encompassing whole nuclei. Primary antibodies used were rabbit anti-HIM-3 (Zetka et al. 1999) and rabbit anti-H3S10p (Upstate 05-598). In D, whole worms were fixed with Carnoy fixative and stained with DAPI as described (Villeneuve 1994), and images were acquired using conventional fluorescence microscopy at a single focal plane. Bar in D, 20 μm.