Figure 1.
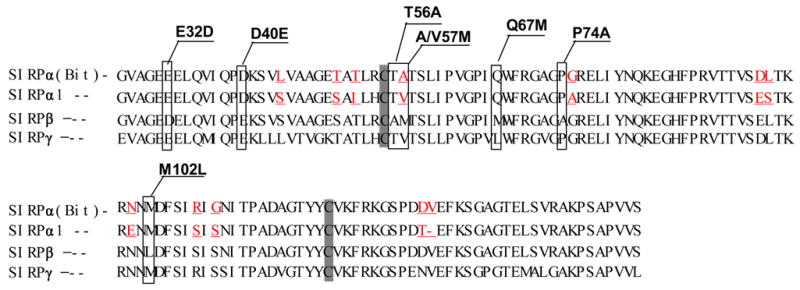
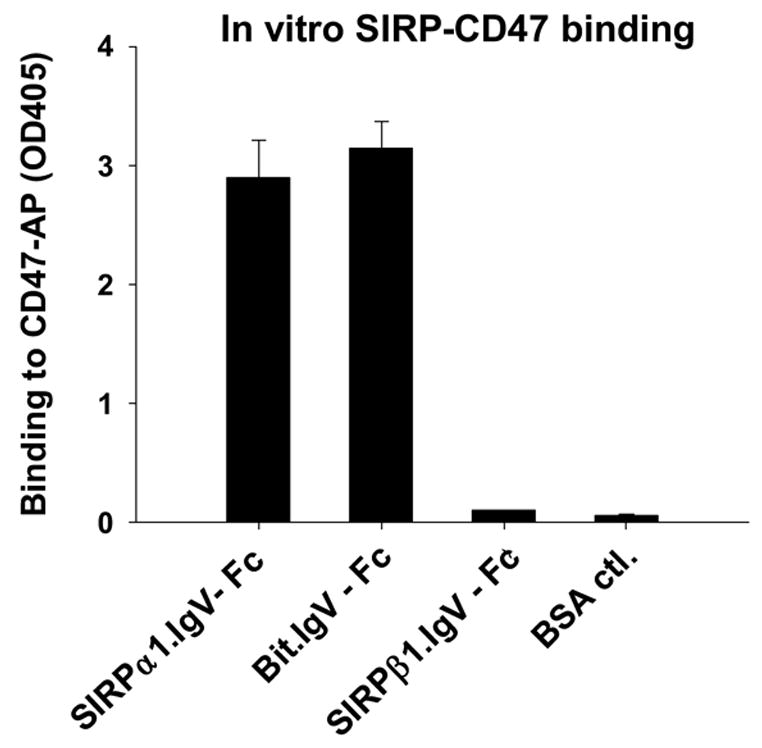
Extracellular binding interactions of SIRP family proteins mediated by the membrane distal IgV domains. A) Primary structure alignments of the extracellular most distal IgV loops of SIRPα members, Bit and SIRPα1, reveal 12 amino acid differences (labeled in red) between these two SIRPα members. The sequence alignments also reveal 7 amino acid (selectively labeled) differences between SIRPα isoforms and SIRPβ1. The primary structure of SIRPγ IgV is also aligned. The shaded Cys residues form the putative disulfide bond in the IgV structures. B) In vitro SIRP-CD47 binding assays. In these experiments, SIRP.IgV-Fc fusion proteins were generated by transfection of COS cells followed by protein purification using protein-A sepharose. The purified fusion proteins (5μg/ml) were used to coat the microtiter wells. After blocking, the wells were incubated with CD47-AP (5μg /ml). After washing, CD47-AP binding to immobilized SIRP.IgV-Fc was detected by assaying AP activity. The data shows that the IgV domains of SIRPα (Bit and SIRPα1), but not SIRPβ1, bind to CD47 extracellular domain fusion protein (CD47-AP).
