Figure 9.
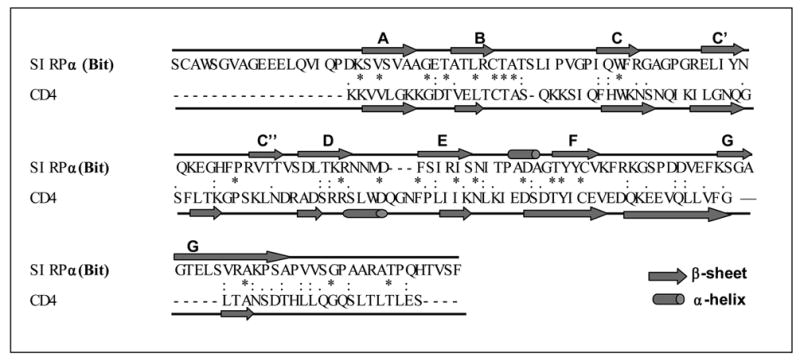
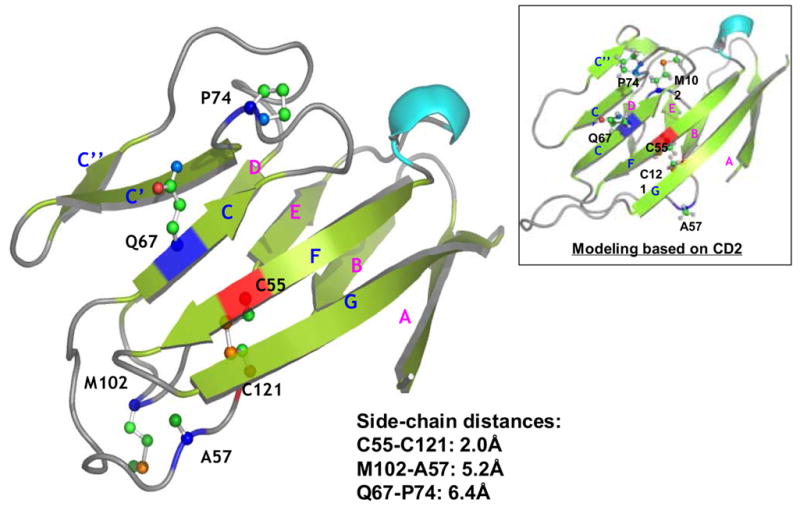
Computational homology modeling of SIRPα (Bit) extracellular IgV domain. A) Sequence alignment of SIRPα (Bit) with CD4. The predicted secondary structural elements, α-helices and βsheets, are shown as rods and arrows, respectively (“*”, identical residues; “:”, highly homologous residues; “.”, homologous residues). B) The predicted three-dimensional model of the Bit IgV domain based on the structures of CD4. The putative disulfide bond in the IgV structure is linked by the corresponding cysteine residues C55 and C121 (red). Q67 is located in the C β-sheet strand and A57 in the loop between the B and C strands. Met102 is predicted in the flexible loop between strands D and E. Another potential residue, Pro74, is predicted in the loop between strands of C and C’. The distances between the side-chains of individual residues are listed. Figure inset shows the result of protein modeling based on the structure of CD2 revealing another possible position of Met102 within the flexible D–E loop.
