Figure 2.
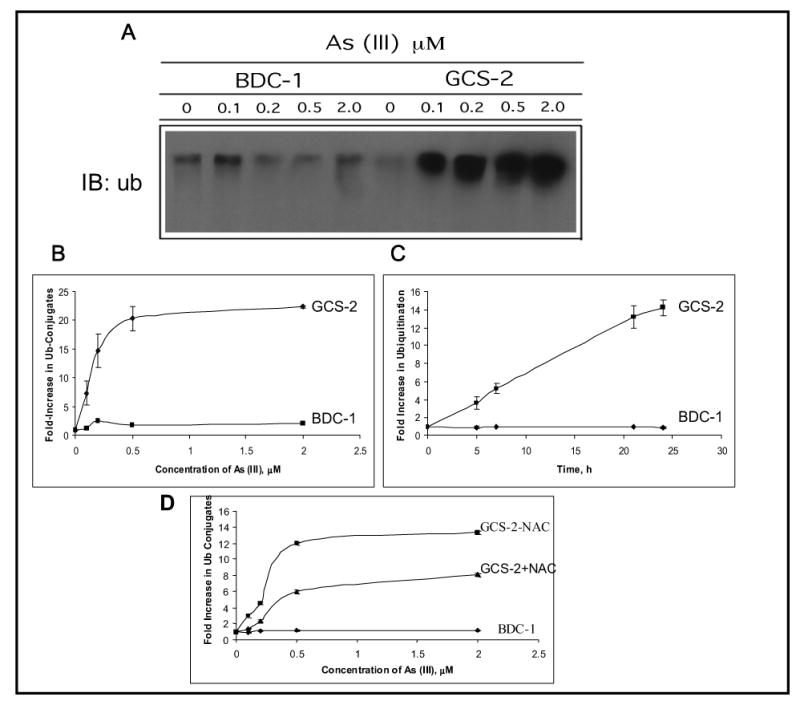
Effect of arsenite on protein ubiquitination in BDC-1 and GCS-2 cells. (A) Dose dependence of arsenite-induced ubiquitination in BDC-1 and GCS-2 cells. GCS-2 cells were plated at 1.5 x 106 cells/dish in the presence of GSH for 48 h. GSH was withdrawn from GCS-2 cells for 24 h and both cell types were treated with various concentrations of arsenite for 21 h. Cell extracts were prepared and 10 μg total protein was separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by immunoblot with polyclonal antibody against ubiquitin. (B) Quantification of the ubiquitin-protein conjugates by densitometry. Blots from (A) were then quantified to measure the high molecular weight ubiquitin-protein conjugates using a densitometer. Each point is an average of three independent determinations. (C) Time-dependent increase in the high molecular weight conjugates at 0.5 μM arsenite treatment. The experimental conditions used were as described in A, except cells were treated for various time points with 0.5μM arsenite. The blots were quantified as described in B. (D) Effect of NAC on arsenite-induced ubiquitination in BDC-1 and GCS-2 cells. GCS-2 cells were grown in the presence of 2 mM NAC for 48 h and divided into two groups: one group was grown in NAC for an additional 24 h in the presence of NAC and treated with 0.5 μM arsenite for 21 h. In a parallel experiment, NAC was withdrawn for 24 h from GCS-2 cells that were grown in the presence of NAC for 48 h and the cells were treated with various concentrations of arsenite for 21 h in the absence of NAC. Fold increase in ubiquitin conjugates were quantified as described in Fig. 2B.
