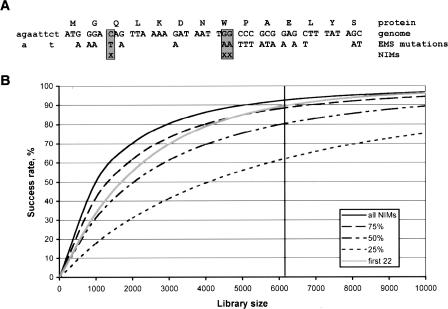
Figure 4.
Nonsense introducing mutations (NIMs) and genome-wide NIM-based knockout screening. (A) A NIM is defined by those positions in the genome that introduce a premature stop codon in the open reading frame of a gene upon mutation. In this example, only a small fraction of the positions that can be mutated by EMS results in the introduction of a stop codon (boxed positions). (B) Success rate for genome-wide knockout retrieval. The percentage of all C. elegans genes with an expected nonsense mutation is plotted as a function of the library size screened. Rates are plotted for all NIMs (all), the first 25%, 50%, and 75% of the NIMs per gene, and the first maximum of 22 NIMs per gene (first 22). Only G/C-to-A/T mutations (mutation frequency one per 46,000 GC-base) are taken into account for this calculation. The vertical line indicates the size of the current library.