Figure 1.
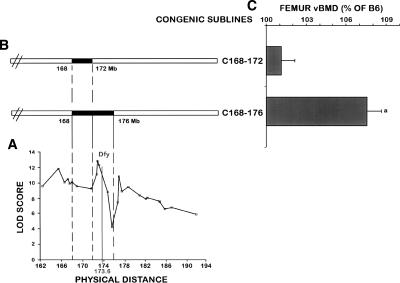
Genetic localization of the Darc gene and BMD phenotype of the two congenic sublines C168–172 and C168–176. (A) Fine mapping of BMD QTL in chromosome 1 using 33 polymorphic markers. Linkage analyses showed three peaks suggesting at least three BMD QTLs within Chr 1. The X-axis represents the physical distance beginning with the centromeric side and extending toward the telomeric side of Chr 1, starting from marker D1mit106 at 162.33 Mb according to the National Center for Biotechnology Information database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/). The Y-axis represents the likelihood values for the presence of a segregating QTL at each marker (LOD score). Genetic localization of the Darc gene within the second BMD QTL (Bmd1b) is indicated. (B) Solid bars represent the CAST chromosomal regions carried by each congenic sublines. (C) Femoral vBMD at the mid-diaphysis of the two sublines C168–172 and C168–176 compared with B6 control mice. Each congenic subline is presented (C, referring to the cast allele), followed by the position (in megabases) of the two markers flanking the donated CAST segment. We designated the congenic subline B6.CAST-1D1mit370-D1mit403 as C168–176, which indicates the approximate proximal and distal megabase limits known for the CAST chromosomal region, and the congenic subline B6.CAST-1D1mit370-D1mit113 was designated as C168–172. Data are expressed as a percentage of B6 and are mean ± SEM. (a) P < 0.01 as measured by Student’s t-test in congenic subline vs. B6 mice. n = 10–14.